Highly Sensitive and Selective Detection of L-Tryptophan by ECL Using Boron-Doped Diamond Electrodes
- PMID: 38894416
- PMCID: PMC11175342
- DOI: 10.3390/s24113627
Highly Sensitive and Selective Detection of L-Tryptophan by ECL Using Boron-Doped Diamond Electrodes
Abstract
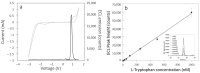
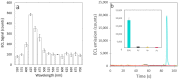
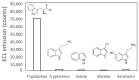
L-tryptophan is an amino acid that is essential to the metabolism of humans. Therefore, there is a high interest for its detection in biological fluids including blood, urine, and saliva for medical studies, but also in food products. Towards this goal, we report on a new electrochemiluminescence (ECL) method for L-tryptophan detection involving the in situ production of hydrogen peroxide at the surface of boron-doped diamond (BDD) electrodes. We demonstrate that the ECL response efficiency is directly related to H2O2 production at the electrode surface and propose a mechanism for the ECL emission of L-tryptophan. After optimizing the analytical conditions, we show that the ECL response to L-tryptophan is directly linear with concentration in the range of 0.005 to 1 µM. We achieved a limit of detection of 0.4 nM and limit of quantification of 1.4 nM in phosphate buffer saline (PBS, pH 7.4). Good selectivity against other indolic compounds (serotonin, 3-methylindole, tryptamine, indole) potentially found in biological fluids was observed, thus making this approach highly promising for quantifying L-tryptophan in a broad range of aqueous matrices of interest.
Keywords: L-tryptophan; boron-doped diamond; electrochemiluminescence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Electrogenerated chemiluminescence of luminol at a boron-doped diamond electrode for the detection of hypochlorite.Analyst. 2022 Jun 13;147(12):2696-2702. doi: 10.1039/d2an00540a. Analyst. 2022. PMID: 35608289
-
Hydrogen peroxide regulated split-type electrochemiluminescence sensing platform for non-invasive detection of gastric cancer-associated D-amino acids.Anal Chim Acta. 2025 Jun 15;1355:344010. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2025.344010. Epub 2025 Apr 2. Anal Chim Acta. 2025. PMID: 40274333
-
Sensitive electrochemical sensor of levofloxacin using boron-doped diamond (BDD) electrode modified with Ti3C2TX (MXene) material.J Food Drug Anal. 2024 Sep 13;32(3):348-357. doi: 10.38212/2224-6614.3517. J Food Drug Anal. 2024. PMID: 39636777 Free PMC article.
-
Electrogenerated chemiluminescence at boron-doped diamond electrodes.Chem Commun (Camb). 2023 Jun 22;59(51):7900-7910. doi: 10.1039/d3cc01507f. Chem Commun (Camb). 2023. PMID: 37249438 Review.
-
Boron-doped diamond electrochemical biosensors.Clin Chim Acta. 2025 Jun 15;574:120285. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2025.120285. Epub 2025 Apr 10. Clin Chim Acta. 2025. PMID: 40220983 Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Protein and Amino Acid Requirements in Human Nutrition: Report of a Joint WHO/FAO/UNU Expert Consultation. WHO Press; Geneva, Switzerland: 2007. p. 150.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

