Dual Stream Long Short-Term Memory Feature Fusion Classifier for Surface Electromyography Gesture Recognition
- PMID: 38894423
- PMCID: PMC11175185
- DOI: 10.3390/s24113631
Dual Stream Long Short-Term Memory Feature Fusion Classifier for Surface Electromyography Gesture Recognition
Abstract
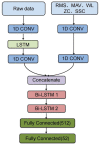
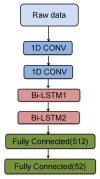
Gesture recognition using electromyography (EMG) signals has prevailed recently in the field of human-computer interactions for controlling intelligent prosthetics. Currently, machine learning and deep learning are the two most commonly employed methods for classifying hand gestures. Despite traditional machine learning methods already achieving impressive performance, it is still a huge amount of work to carry out feature extraction manually. The existing deep learning methods utilize complex neural network architectures to achieve higher accuracy, which will suffer from overfitting, insufficient adaptability, and low recognition accuracy. To improve the existing phenomenon, a novel lightweight model named dual stream LSTM feature fusion classifier is proposed based on the concatenation of five time-domain features of EMG signals and raw data, which are both processed with one-dimensional convolutional neural networks and LSTM layers to carry out the classification. The proposed method can effectively capture global features of EMG signals using a simple architecture, which means less computational cost. An experiment is conducted on a public DB1 dataset with 52 gestures, and each of the 27 subjects repeats every gesture 10 times. The accuracy rate achieved by the model is 89.66%, which is comparable to that achieved by more complex deep learning neural networks, and the inference time for each gesture is 87.6 ms, which can also be implied in a real-time control system. The proposed model is validated using a subject-wise experiment on 10 out of the 40 subjects in the DB2 dataset, achieving a mean accuracy of 91.74%. This is illustrated by its ability to fuse time-domain features and raw data to extract more effective information from the sEMG signal and select an appropriate, efficient, lightweight network to enhance the recognition results.
Keywords: deep learning; dual stream LSTM; feature fusion; gesture recognition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures










References
-
- Pratt J., Krupp B., Morse C., Collins S. The RoboKnee: An exoskeleton for enhancing strength and endurance during walking; Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2004. Proceedings. ICRA ’04. 2004; New Orleans, LA, USA. 26 April–1 May 2004; pp. 2430–2435. - DOI
-
- Fu R., Zhang B., Liang H., Wang S., Wang Y., Li Z. Gesture recognition of sEMG signal based on GASF-LDA feature enhancement and adaptive ABC optimized SVM. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2023;85:105104. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2023.105104. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

