An Integrated Smart Pond Water Quality Monitoring and Fish Farming Recommendation Aquabot System
- PMID: 38894471
- PMCID: PMC11175198
- DOI: 10.3390/s24113682
An Integrated Smart Pond Water Quality Monitoring and Fish Farming Recommendation Aquabot System
Abstract
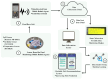
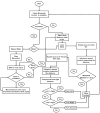
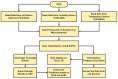
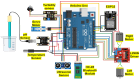
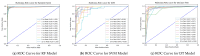
The integration of cutting-edge technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), robotics, and machine learning (ML) has the potential to significantly enhance the productivity and profitability of traditional fish farming. Farmers using traditional fish farming methods incur enormous economic costs owing to labor-intensive schedule monitoring and care, illnesses, and sudden fish deaths. Another ongoing issue is automated fish species recommendation based on water quality. On the one hand, the effective monitoring of abrupt changes in water quality may minimize the daily operating costs and boost fish productivity, while an accurate automatic fish recommender may aid the farmer in selecting profitable fish species for farming. In this paper, we present AquaBot, an IoT-based system that can automatically collect, monitor, and evaluate the water quality and recommend appropriate fish to farm depending on the values of various water quality indicators. A mobile robot has been designed to collect parameter values such as the pH, temperature, and turbidity from all around the pond. To facilitate monitoring, we have developed web and mobile interfaces. For the analysis and recommendation of suitable fish based on water quality, we have trained and tested several ML algorithms, such as the proposed custom ensemble model, random forest (RF), support vector machine (SVM), decision tree (DT), K-nearest neighbor (KNN), logistic regression (LR), bagging, boosting, and stacking, on a real-time pond water dataset. The dataset has been preprocessed with feature scaling and dataset balancing. We have evaluated the algorithms based on several performance metrics. In our experiment, our proposed ensemble model has delivered the best result, with 94% accuracy, 94% precision, 94% recall, a 94% F1-score, 93% MCC, and the best AUC score for multi-class classification. Finally, we have deployed the best-performing model in a web interface to provide cultivators with recommendations for suitable fish farming. Our proposed system is projected to not only boost production and save money but also reduce the time and intensity of the producer's manual labor.
Keywords: Internet of Things (IoT); machine learning; real-time water quality; smart fish farming; smart robot; solar power.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of Interest.
Figures








References
-
- Ahmed M., Rahaman M.O., Rahman M., Abul Kashem M. Analyzing the Quality of Water and Predicting the Suitability for Fish Farming based on IoT in the Context of Bangladesh; Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Sustainable Technologies for Industry 4.0 (STI); Dhaka, Bangladesh. 24–25 December 2019; pp. 1–5. - DOI
-
- Zulkifli C.Z., Garfan S., Talal M., Alamoodi A.H., Alamleh A., Ahmaro I.Y.Y., Sulaiman S., Ibrahim A.B., Zaidan B.B., Ismail A.R., et al. IoT-Based Water Monitoring Systems: A Systematic Review. Water. 2022;14:3621. doi: 10.3390/w14223621. - DOI
-
- Zainuddin Z., Idris R., Azis A. Water Quality Monitoring System for Vannamae Shrimp Cultivation Based on Wireless Sensor Network In Taipa, Mappakasunggu District, Takalar; Proceedings of the First International Conference on Materials Engineering and Management—Engineering Section (ICMEMe 2018); Makassar, Indonesia. 1 August 2018; - DOI
-
- Agossou B.E., Toshiro T. IoT & AI Based System for Fish Farming: Case study of Benin; Proceedings of the Conference on Information Technology for Social Good; Rome, Italy. 9–11 September 2021; pp. 259–264. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

