Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Effects of Marine Phlorotannins and Bromophenols Supportive of Their Anticancer Potential
- PMID: 38894623
- PMCID: PMC11819485
- DOI: 10.1093/nutrit/nuae066
Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Effects of Marine Phlorotannins and Bromophenols Supportive of Their Anticancer Potential
Abstract
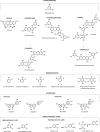
Following the goal of optimizing nutrition, the food industry has been continuously working on food reformulation, nutritional patterns, functional foods development, and the general promotion of a healthy lifestyle. To this end, the scientific community has been increasingly investigating natural compounds that could prevent or treat chronic diseases. Phlorotannins and bromophenols are phenolic compounds particularly present in marine organisms. There is extensive evidence that shows their potential in the prevention of noncommunicable diseases, including cancer, the second cause of mortality worldwide. Numerous studies have demonstrated the anticarcinogenic activity of polyphenolic algae compounds both in cell culture and experimental animal models. Although recent reviews are also available, the present update focuses on the most recent findings related to the antioxidant/anti-inflammatory effect of seaweed phenolics, as well as their regulatory capacity for new molecular targets. Additionally, the review addresses and discusses the close link between inflammation and oxidative stress, along with their relationship with tumor onset and progression, including the most recent findings supporting this correlation. Although clinical studies are still needed to support this evidence, phlorotannins and bromophenols constitute an emerging bioactive group with high potential as chemopreventive agents and/or potential adjuvants for existing cancer therapies.
Keywords: anti-inflammatory activity; antioxidant activity; bromophenols; cancer; marine organisms; phlorotannins.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the International Life Sciences Institute.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Ferlay J, Ervik M, Lam F, et al.Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2020. Accessed February 2021. https://gco.iarc.fr/today
-
- Lefranc F, Koutsaviti A, Ioannou E, et al.Algae metabolites: from in vitro growth inhibitory effects to promising anticancer activity. Nat Prod Rep. 2019;36(5):810-841. - PubMed
-
- Erpel F, Mateos R, Pérez-Jiménez J, Pérez-Correa JR.. Phlorotannins: from isolation and structural characterization, to the evaluation of their antidiabetic and anticancer potential. Food Res Int. 2020;137:109589. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical