The Regulation of Metabolic Homeostasis by Incretins and the Metabolic Hormones Produced by Pancreatic Islets
- PMID: 38894706
- PMCID: PMC11184168
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S415934
The Regulation of Metabolic Homeostasis by Incretins and the Metabolic Hormones Produced by Pancreatic Islets
Abstract
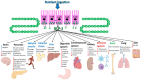
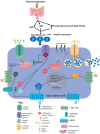
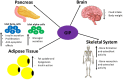
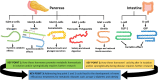
In healthy humans, the complex biochemical interplay between organs maintains metabolic homeostasis and pathological alterations in this process result in impaired metabolic homeostasis, causing metabolic diseases such as diabetes and obesity, which are major global healthcare burdens. The great advancements made during the last century in understanding both metabolic disease phenotypes and the regulation of metabolic homeostasis in healthy individuals have yielded new therapeutic options for diseases like type 2 diabetes (T2D). However, it is unlikely that highly desirable more efficacious treatments will be developed for metabolic disorders until the complex systemic regulation of metabolic homeostasis becomes more intricately understood. Hormones produced by pancreatic islet beta-cells (insulin) and alpha-cells (glucagon) are pivotal for maintaining metabolic homeostasis; the activity of insulin and glucagon are reciprocally correlated to achieve strict control of glucose levels (normoglycaemia). Metabolic hormones produced by other pancreatic islet cells and incretins produced by the gut are also crucial for maintaining metabolic homeostasis. Recent studies highlighted the incomplete understanding of metabolic hormonal synergism and, therefore, further elucidation of this will likely lead to more efficacious treatments for diseases such as T2D. The objective of this review is to summarise the systemic actions of the incretins and the metabolic hormones produced by the pancreatic islets and their interactions with their respective receptors.
Keywords: GLP-1; GLP-1R; glucagon; incretin; insulin; metabolism; obesity; type 2 diabetes.
© 2024 Reed et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

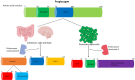
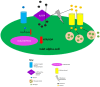
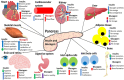
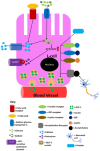
Similar articles
-
Impact of incretin therapy on islet dysfunction: an underlying defect in the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes.Postgrad Med. 2009 Jan;121(1):46-58. doi: 10.3810/pgm.2009.01.1954. Postgrad Med. 2009. PMID: 19179813
-
Incretins.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2016;233:137-71. doi: 10.1007/164_2015_9. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 25903418 Review.
-
Pancreatic islet dysfunction in type 2 diabetes: a rational target for incretin-based therapies.Curr Med Res Opin. 2007 Apr;23(4):933-44. doi: 10.1185/030079906x167336. Curr Med Res Opin. 2007. PMID: 17407650 Review.
-
[Incretin hormones in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Part I: influence of insulinotropic gut-derived hormones (incretins) on glucose metabolism].Endokrynol Pol. 2007 Nov-Dec;58(6):522-8. Endokrynol Pol. 2007. PMID: 18205109 Review. Polish.
-
Genetic determinants of circulating GIP and GLP-1 concentrations.JCI Insight. 2017 Nov 2;2(21):e93306. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.93306. JCI Insight. 2017. PMID: 29093273 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Affourtit C. Mitochondrial involvement in skeletal muscle insulin resistance: a case of imbalanced bioenergetics. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 2016;1857(10):1678–1693. - PubMed
-
- Voet D, Voet J. Biochemistry. 4th ed. New York: Wiley & Sons; 2011.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

