Integrating proteomics and explainable artificial intelligence: a comprehensive analysis of protein biomarkers for endometrial cancer diagnosis and prognosis
- PMID: 38894711
- PMCID: PMC11184912
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1389325
Integrating proteomics and explainable artificial intelligence: a comprehensive analysis of protein biomarkers for endometrial cancer diagnosis and prognosis
Abstract
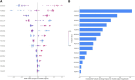
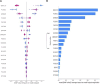
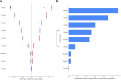
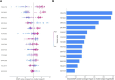
Endometrial cancer, which is the most common gynaecological cancer in women after breast, colorectal and lung cancer, can be diagnosed at an early stage. The first aim of this study is to classify age, tumor grade, myometrial invasion and tumor size, which play an important role in the diagnosis and prognosis of endometrial cancer, with machine learning methods combined with explainable artificial intelligence. 20 endometrial cancer patients proteomic data obtained from tumor biopsies taken from different regions of EC tissue were used. The data obtained were then classified according to age, tumor size, tumor grade and myometrial invasion. Then, by using three different machine learning methods, explainable artificial intelligence was applied to the model that best classifies these groups and possible protein biomarkers that can be used in endometrial prognosis were evaluated. The optimal model for age classification was XGBoost with AUC (98.8%), for tumor grade classification was XGBoost with AUC (98.6%), for myometrial invasion classification was LightGBM with AUC (95.1%), and finally for tumor size classification was XGBoost with AUC (94.8%). By combining the optimal models and the SHAP approach, possible protein biomarkers and their expressions were obtained for classification. Finally, EWRS1 protein was found to be common in three groups (age, myometrial invasion, tumor size). This article's findings indicate that models have been developed that can accurately classify factors including age, tumor grade, and myometrial invasion all of which are critical for determining the prognosis of endometrial cancer as well as potential protein biomarkers associated with these factors. Furthermore, we were able to provide an analysis of how the quantities of the proteins suggested as biomarkers varied throughout the classes by combining the SHAP values with these ideal models.
Keywords: biomarker; endometrium cancer; explainable artificial intelligence; machine learning; proteomic.
Copyright © 2024 Yasar, Yagin, Melekoglu and Ardigò.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Applicability of Artificial Intelligence in Predicting the Depth of Myometrial Invasion on MRI Studies-A Systematic Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Aug 3;13(15):2592. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13152592. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37568955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peripheral blood mononuclear cell derived biomarker detection using eXplainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) provides better diagnosis of breast cancer.Comput Biol Chem. 2023 Jun;104:107867. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2023.107867. Epub 2023 Apr 3. Comput Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 37030103
-
Cancer Metastasis Prediction and Genomic Biomarker Identification through Machine Learning and eXplainable Artificial Intelligence in Breast Cancer Research.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Oct 26;13(21):3314. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13213314. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37958210 Free PMC article.
-
Explainable artificial intelligence model for identifying COVID-19 gene biomarkers.Comput Biol Med. 2023 Mar;154:106619. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.106619. Epub 2023 Feb 1. Comput Biol Med. 2023. PMID: 36738712 Free PMC article.
-
MELF pattern of myometrial invasion and role in possible endometrial cancer diagnostic pathway: A systematic review of the literature.Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2018 Nov;230:147-152. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2018.09.036. Epub 2018 Sep 25. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2018. PMID: 30286364
Cited by
-
First-Trimester Preeclampsia-Induced Disturbance in Maternal Blood Serum Proteome: A Pilot Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 3;25(19):10653. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910653. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408980 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aksoy S., Özavşar M., Altındal A. (2022). Classification of VOC vapors using machine learning algorithms. J. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. 7 (2), 97–107. 10.30931/jetas.1030981 - DOI
-
- Arrieta A. B., Díaz-Rodríguez N., Del Ser J., Bennetot A., Tabik S., Barbado A., et al. (2020). Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI): concepts, taxonomies, opportunities and challenges toward responsible AI. Inf. fusion 58, 82–115. 10.1016/j.inffus.2019.12.012 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

