A Comprehensive Pan-Cancer Analysis Reveals Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor 2A Gene as a Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker in Colon Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 38894777
- PMCID: PMC11184547
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.60586
A Comprehensive Pan-Cancer Analysis Reveals Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor 2A Gene as a Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker in Colon Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
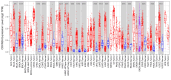
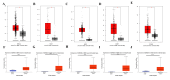
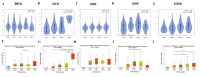
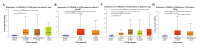
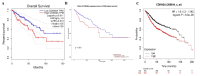
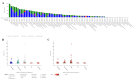
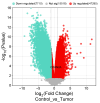
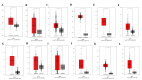
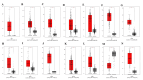
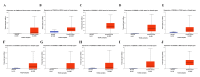
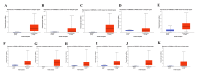
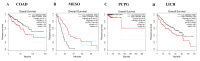
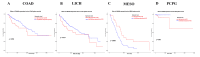
Introduction Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A (CDKN2A) is a suppressor carcinogenic gene that is upregulated across various types of cancer including breast, liver, thyroid, and bile duct cancer due to its crucial role in cell cycle regulation and cell division. Nevertheless, it is mostly investigated at the genetic level, but it is still poorly studied on pan-cancer analysis as a biomarker and this study shows its significant potential diagnostic and prognostic characteristics. However, this study aims to investigate the role of CDKN2A as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker across various types of cancer focusing primarily on colon adenocarcinoma (COAD). Methods We investigated CDKN2A gene expression in a pan-cancer analysis across different types of cancer to show its diagnostic potential characteristics by using various bioinformatic tools, including Tumor Immune Estimation Resource (TIMER) 2.0, Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis (GEPIA), and University of Alabama at Birmingham Cancer Data Analysis Portal (UALCAN) database. TIMER was used to profile gene expression across 32 types of cancer composed of 10,000 RNA-seq samples obtained from the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and to analyze the tumor-infiltrating immune cells. In addition, GEPIA and UALCAN were further used to analyze gene expression, in terms of gene regulation, pathological stages, and clinical parameters, including gender, age, and race. Therefore, we used GEPIA, UALCAN, and Kaplan-Meier plotter particularly across adenocarcinoma to investigate CDKN2A prognosis by studying its high expression association with the patient's overall survival rate to show the tumor progression. Then, we looked into the genetic alteration of CDKN2A by using the cBio Cancer Genomics Portal (cBioPortal), including 10 pan-cancer studies. We concluded the analysis with gene validation by using a public cohort in Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO). Results CDKN2A showed a trend of upregulation in most cancers and it was significantly upregulated in five cancers, which were commonly identifiable in three databases, including breast invasive carcinoma (p < 0.001), kidney chromophobe (p < 0.001), kidney renal clear cell carcinoma (p < 0.001), kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma (p < 0.001), and COAD (p < 0.001). The upregulation was significantly different in association with pathogenic stages II and III (pr(>F) = 0.00234) which was identifiable significantly in COAD more than in other cancers. The gene showed a high upregulation in association with poor prognosis of patient survival in three cancers, including COAD (log-rank p = 0.011), mesothelioma (log-rank p = 5.9e-07), and liver hepatocellular carcinoma (log-rank p = 0.0045). Therefore, COAD was the only comprehensively analyzed tumor to show a diagnostic and prognostic potential characteristic during high upregulation of CDKN2A. Furthermore, CDKN2A displayed a rare mutation in the form of deep deletion (9%) and revealed an upregulation associated with CD4+ T cells (p = 0.0108), macrophage (p = 0.0073), and neutrophils (p = 0.0272) as immune cells infiltrating COAD. Conclusion Our study demonstrates the pan-cancer relevance of CDKN2A and revealed a novelty in showing CDKN2A underscores its potential as a diagnostic prognostic biomarker in COAD since CDKN2A is mostly studied at a genetic level across COAD.
Keywords: cancer biomarker; cancer genomic profiling; cdkn2a; cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2a; diagnostic marker; overexpression; prognostic markers.
Copyright © 2024, Salem et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- INK4 proteins, a family of mammalian CDK inhibitors with novel biological functions. Cánepa ET, Scassa ME, Ceruti JM, Marazita MC, Carcagno AL, Sirkin PF, Ogara MF. IUBMB Life. 2007;59:419–426. - PubMed
-
- Sequence variation and chromosomal mapping of the murine Cdkn2a tumor suppressor gene. Herzog CR, You M. Mamm Genome. 1997;8:65–66. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
