Two Distinct Characteristics of Immune Microenvironment in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Wnt/β-Catenin Mutations
- PMID: 38894812
- PMCID: PMC11185857
- DOI: 10.1159/000533818
Two Distinct Characteristics of Immune Microenvironment in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Wnt/β-Catenin Mutations
Abstract
Introduction: Immunotherapy is becoming a promising approach for unresectable-hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); the anti-tumor response is affected by the tumor microenvironment (TME). Although Wnt/β-catenin mutations are reported to cause non-inflamed phenotype, their role on TME remains controversial. We aimed to clarify the heterogeneity of immunophenotype in HCC with Wnt/β-catenin mutations.
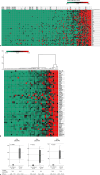
Methods: This study includes 152 resected HCCs; mutations in the catenin beta-1, adenomatous polyposis coli, or AXIN1, or AXIN2 genes were defined as Wnt/β-catenin mutations. With hierarchical cluster analyses, TME was classified into inflamed or non-inflamed classes based on the gene expressions associated with T-cell activation. Expression profiles of molecules related to cell differentiation and biliary-stem cell markers were compared between the TME classes to investigate whether differences in tumor traits were associated with TME.
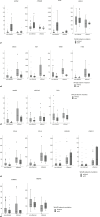
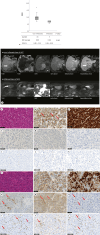
Results: Forty of 152 (26.3%) HCCs carried the Wnt/β-catenin mutations. Of these, 33 were classified as non-inflamed (33/40, 82.5%) and 7 as inflamed (7/40, 17.5%). Non-inflamed class was characterized by low number of CD3+, CD4+, and CD8+ cells on immunostaining, and high mRNA expressions of AXIN2 and GLUL, which are involved in the canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling and hepatocyte differentiation, respectively. Non-inflamed tumors showed higher enhancement on the hepatobiliary-phase of gadolinium-ethoxybenzyl-diethylenetriamine (Gd-EOB-DTPA)-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) compared to inflamed tumors. HCCs classified as inflamed class are revealed to have high numbers of CD3+, CD4+, and CD8+ tumor infiltrating lymphocytes on immunostaining. This class is associated with increased expression of anti-epithelial cell adhesion molecule and FOXM1 accompanied by upregulation of genes related to interferon-gamma signaling, dendritic cell migration, regulatory T cells, and myeloid-derived suppressor cell activation and recognized as low enhancement nodule on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI.
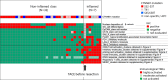
Conclusion: Heterogeneity of tumor traits and TME was observed in HCC with Wnt/β-catenin mutation. The potential was indicated that tumor traits and TME are determined not only by the activation of the HNF4A but also by FOXM1, both of which are downstream transcription factor of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; Inflamed tumors; Non-inflamed tumors; Tumor microenvironment; Wnt/β-catenin mutation.
© 2023 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
N.N. is an Editorial Board member of liver cancer. T.A., Y.K., K.S., M.M., H.C., M.T., S.H., H.I., K.U., Y.M. M.T., T.N., and K.N. have no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose. S.M. Michie Sakamoto is an Associate Editor of Liver Cancer. M.K. has received grants from Taiho Pharmaceuticals, Chugai Pharmaceuticals, Otsuka, Takeda, Sumitomo Dainippon-Sumitomo, Daiichi Sankyo, AbbVie, Astellas Pharma, and Bristol-Myers Squibb. M.K. has also received grants and personal lecture fees from Merck Sharpe and Dohme (M.S.D), Eisai, and Bayer, and is an adviser for MSD, Eisai, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Chugai, AstraZeneca and ONO Pharmaceuticals. Masatoshi Kudo is an Editor-in-Chief of liver cancer.
Figures

References
-
- Takayama T, Yamazaki S, Matsuyama Y, Midorikawa Y, Shiina S; Liver Cancer Study Group of Japan, et al. Prognostic grade for resecting hepatocellular carcinoma: multicentre retrospective study. Br J Surg. 2021 Apr 30;108(4):412–8. - PubMed
-
- Finn RS, Qin S, Ikeda M, Galle PR, Ducreux M, Kim TY, et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med Overseas Ed. 2020 May 14;382(20):1894–905. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

