Conjugated Nonionic Detergent Micelles: An Efficient Purification Platform for Dimeric Human Immunoglobulin A
- PMID: 38894919
- PMCID: PMC11181477
- DOI: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.4c00128
Conjugated Nonionic Detergent Micelles: An Efficient Purification Platform for Dimeric Human Immunoglobulin A
Abstract
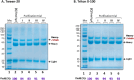
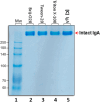
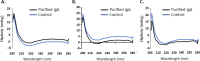
The SARS-COV-2 virus is a deadly agent of inflammatory respiratory disease. Since 2020, studies have focused on developing new therapies based on galactose-rich IgA antibodies. Clinical surveys have also revealed that galactose-deficient IgA1 polymerizes in serum, producing IgA nephropathy, which is a common cause of kidney failure in young adults. Here we show that IgA1-IgA2 dimers are efficiently and economically purified in solution via conjugated nonionic surfactant micellar aggregates. Quantitative capture at pH 7 and extraction at pH 6.5 can avoid antibody exposure to acidic, potentially denaturing conditions. Brij-O20 aggregates lead to the highest process yields (88-91%) and purity (94%). Recovered IgA dimers preserve their native secondary structure and do not self-associate. Increasing the reaction volume has little impact on yield or purity. By introducing an efficient, inexpensive IgA purification protocol, we assist pharmaceutical firms and research laboratories in developing new IgA-based therapies as well as in increasing our understanding of IgA1 polymerization.
© 2024 American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




References
-
- Bioley G.; Monnerat J.; Lötscher M.; Vonarburg C.; Zuercher A.; Corthésy B. Plasma-Derived Polyreactive Secretory-Like IgA and IgM Opsonizing Salmonella enterica Typhimurium Reduces Invasion and Gut Tissue Inflammation through Agglutination. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1043. 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01043. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pasquier B.; Launay P.; Kanamaru Y.; Moura I. C.; Pfirsch S.; Ruffié C.; Hénin D.; Benhamou M.; Pretolani M.; Blank U.; Monteiro R. C. Identification of FcalphaRI as an inhibitory receptor that controls inflammation: dual role of FcRgamma ITAM. Immunity 2005, 22 (1), 31–42. 10.1016/j.immuni.2004.11.017. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rossato E.; Ben Mkaddem S.; Kanamaru Y.; Hurtado-Nedelec M.; Hayem G.; Descatoire V.; Vonarburg C.; Miescher S.; Zuercher A. W.; Monteiro R. C. Reversal of Arthritis by Human Monomeric IgA Through the Receptor-Mediated SH2 Domain-Containing Phosphatase 1 Inhibitory Pathway. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67 (7), 1766–77. 10.1002/art.39142. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

