Radiofrequency ablation compared to surgery for thyroid nodules: A case for office based treatment
- PMID: 38895024
- PMCID: PMC11184567
- DOI: 10.1002/lio2.1276
Radiofrequency ablation compared to surgery for thyroid nodules: A case for office based treatment
Abstract
Objective: We aim to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of radiofrequency ablation (RFA) for benign thyroid nodules by ENT surgeons and to compare it to conventional hemithyroidectomy in the public healthcare, operating theater contained setting.
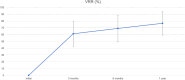
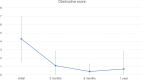
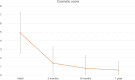
Methods: 50 patients who underwent a single session of RFA for symptomatic benign thyroid nodules in Prince of Wales Hospital and Tseung Kwan O Hospital in Hong Kong from 2020 to 2022 were evaluated. Objective outcomes including nodule volume, volume reduction rate (VRR) and complications were recorded. Subjective response in the form of a 0-10 point scale for patient symptoms including obstructive, cosmetic, pain and satisfaction scores were collected.
Results: Significant reduction in mean VRR was found at 3, 6 and 12 months post treatment, accompanied by a significant reduction in the mean obstructive and cosmetic symptom scores. Comparing with conventional hemithyroidectomy, the RFA group had a significantly shorter mean procedure time and lower rate of complications. Estimated cost to patient for RFA was found to be less than half of that of hemithyroidectomy.
Conclusion: RFA is a safe and effective treatment modality for benign thyroid nodules by ENT surgeons with advantages of being a scarless local anesthetic procedure with shorter procedure time, lower complication rate and lower cost to patient compared to hemithyroidectomy. In Hong Kong, where most of the population is treated in the public sector, there are limited resources, often with high caseload burden and long operation waiting times. Therefore, RFA is an office-based treatment that serves as a valuable alternative to hemithyroidectomy for benign nodules, especially in lower resource settings.
Level of evidence: 3.
Keywords: RFA; hemithyroidectomy; thyroid nodules.
© 2024 The Author(s). Laryngoscope Investigative Otolaryngology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Triological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Single-session treatment of benign thyroid nodules with radiofrequency ablation: Results at 6 months in 24 patients.Endocrinol Diabetes Nutr (Engl Ed). 2020 Mar;67(3):164-171. doi: 10.1016/j.endinu.2019.06.003. Epub 2019 Aug 19. Endocrinol Diabetes Nutr (Engl Ed). 2020. PMID: 31439500 English, Spanish.
-
[Anhydrous Ethanol Improves Efficiency of Radiofrequency Ablation for the Treatment of Benign Thyroid Nodules:A Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial].Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2020 Jun 30;42(3):331-337. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.11512. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2020. PMID: 32616128 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Safety and Efficacy of Ultrasound-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation for Benign Nonfunctional Thyroid Nodules in Children: A Retrospective Study of 62 Patients with Over Four Years of Follow-Up.Thyroid. 2022 May;32(5):525-535. doi: 10.1089/thy.2021.0454. Epub 2022 Jan 17. Thyroid. 2022. PMID: 34915754
-
Comparison of radiofrequency ablation and microwave ablation for benign thyroid nodules: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2021 Jul;95(1):187-196. doi: 10.1111/cen.14438. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2021. PMID: 33556187
-
Efficacy of thermal ablation in benign non-functioning solid thyroid nodule: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Endocrine. 2020 Jan;67(1):35-43. doi: 10.1007/s12020-019-02019-3. Epub 2019 Jul 20. Endocrine. 2020. PMID: 31327158
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous