Exploring gut microbiota's role in rheumatic valve disease: insights from a Mendelian randomization study and mediation analysis
- PMID: 38895120
- PMCID: PMC11183100
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1362753
Exploring gut microbiota's role in rheumatic valve disease: insights from a Mendelian randomization study and mediation analysis
Abstract
Background: Investigating the relationship between gut microbiota and Rheumatic Valve Disease (RVD) is crucial for understanding the disease's etiology and developing effective interventions. Our study adopts a novel approach to examine the potential causal connections between these factors.
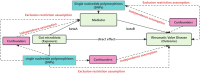
Methods: Utilizing a two-sample Mendelian Randomization (MR) framework, we incorporated a multi-variable MR (MVMR) strategy to assess the mediatory mechanisms involved. This approach involved analyzing data from the MiBioGen consortium for gut microbiota and the FinnGen for RVD, among other sources. Instrumental variables (IVs) were carefully selected based on rigorous MR principles, and statistical analysis was conducted using bidirectional two-sample MR, such as inverse variance-weighted (IVW), weighted median, MR-Egger regression and MR Steiger Test methods. The MR-PRESSO strategy was employed for outlier detection, and MVMR was used to untangle the complex relationships between multiple microbiota and RVD.
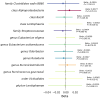
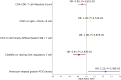
Results: Our analysis highlighted several gut microbiota classes and families with potential protective effects against RVD, including Lentisphaerae, Alphaproteobacteria, and Streptococcaceae. In contrast, certain genera, such as Eubacterium eligens and Odoribacter, were identified as potential risk factors. The MVMR analysis revealed significant mediation effects of various immune cell traits and biomarkers, such as CD4-CD8- T cells, CD3 on Terminally Differentiated CD8+ T cell and Pentraxin-related protein PTX, elucidating the complex pathways linking gut microbiota to RVD.
Conclusion: This study underscores the intricate and potentially causal relationship between gut microbiota and RVD, mediated through a range of immune and hormonal factors. The use of MVMR in our methodological approach provides a more comprehensive understanding of these interactions, highlighting the gut microbiota's potential as therapeutic targets in RVD management. Our findings pave the way for further research to explore these complex relationships and develop targeted interventions for RVD.
Keywords: Mendelian randomization; estradiol; gut microbiota; immune cell; mediation analysis; rheumatic valve disease.
Copyright © 2024 Chen, Hu, Ning and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Exploring blood immune cells in the protective effects of gut microbiota on rheumatic heart disease based on Mendelian randomization analysis.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 28;15(1):10745. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-92356-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40155605 Free PMC article.
-
The causal relationship between gut microbiota and inflammatory dermatoses: a Mendelian randomization study.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 27;14:1231848. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1231848. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37828993 Free PMC article.
-
Gene prediction of immune cells association between gut microbiota and colorectal cancer: a Mendelian randomization study.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 31;16:1460936. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1460936. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39958359 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic liability of gut microbiota for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and lung function: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 May 22;14:1348685. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1348685. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38841114 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the potential causal relationship between gut microbiota and heart failure: A two-sample mendelian randomization study combined with the geo database.Curr Probl Cardiol. 2024 Feb;49(2):102235. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2023.102235. Epub 2023 Nov 30. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38040216 Review.
Cited by
-
Is skimmed milk really heart-healthy?: A mediation Mendelian randomization analysis of coronary risk via serum metabolites.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Aug 22;104(34):e42653. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042653. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40859556 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Available online at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/rheumatic-heart-disease (Accessed 2023 Dec 10).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

