Nanoenzymes: A Radiant Hope for the Early Diagnosis and Effective Treatment of Breast and Ovarian Cancers
- PMID: 38895143
- PMCID: PMC11184228
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S460712
Nanoenzymes: A Radiant Hope for the Early Diagnosis and Effective Treatment of Breast and Ovarian Cancers
Abstract
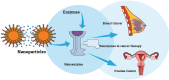
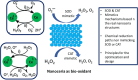
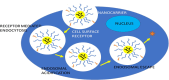
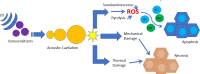
Breast and ovarian cancers, despite having chemotherapy and surgical treatment, still have the lowest survival rate. Experimental stages using nanoenzymes/nanozymes for ovarian cancer diagnosis and treatment are being carried out, and correspondingly the current treatment approaches to treat breast cancer have a lot of adverse side effects, which is the reason why researchers and scientists are looking for new strategies with less side effects. Nanoenzymes have intrinsic enzyme-like activities and can reduce the shortcomings of naturally occurring enzymes due to the ease of storage, high stability, less expensive, and enhanced efficiency. In this review, we have discussed various ways in which nanoenzymes are being used to diagnose and treat breast and ovarian cancer. For breast cancer, nanoenzymes and their multi-enzymatic properties can control the level of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in cells or tissues, for example, oxidase (OXD) and peroxidase (POD) activity can be used to generate ROS, while catalase (CAT) or superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity can scavenge ROS. In the case of ovarian cancer, most commonly nanoceria is being investigated, and also when folic acid is combined with nanoceria there are additional advantages like inhibition of beta galactosidase. Nanocarriers are also used to deliver small interfering RNA that are effective in cancer treatment. Studies have shown that iron oxide nanoparticles are actively being used for drug delivery, similarly ferritin carriers are used for the delivery of nanozymes. Hypoxia is a major factor in ovarian cancer, therefore MnO2-based nanozymes are being used as a therapy. For cancer diagnosis and screening, nanozymes are being used in sonodynamic cancer therapy for cancer diagnosis and screening, whereas biomedical imaging and folic acid gold particles are also being used for image guided treatments. Nanozyme biosensors have been developed to detect ovarian cancer. This review article summarizes a detailed insight into breast and ovarian cancers in light of nanozymes-based diagnostic and therapeutic approaches.
Keywords: breast cancer; diagnosis; nanoenzymes; ovarian cancer; treatment.
© 2024 Shahid et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Nanozyme-based catalytic theranostics.RSC Adv. 2019 Dec 23;10(1):10-20. doi: 10.1039/c9ra09021e. eCollection 2019 Dec 20. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35492517 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-Atom-Based Nanoenzyme in Tissue Repair.ACS Nano. 2024 May 21;18(20):12639-12671. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.4c00308. Epub 2024 May 8. ACS Nano. 2024. PMID: 38718193 Review.
-
Endocytosis of cerium oxide nanoparticles and modulation of reactive oxygen species in human ovarian and colon cancer cells.Acta Biomater. 2017 Mar 1;50:127-141. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.12.010. Epub 2016 Dec 8. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 27940194
-
Smart Biomimetic Nanozymes for Precise Molecular Imaging: Application and Challenges.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Feb 7;16(2):249. doi: 10.3390/ph16020249. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37259396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Will the Bacteria Survive in the CeO2 Nanozyme-H2O2 System?Molecules. 2021 Jun 19;26(12):3747. doi: 10.3390/molecules26123747. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34205408 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Nanomedicine in cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases: targeted nanozyme therapies and their clinical potential and current challenges.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Jul 28;23(1):543. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03590-w. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40717066 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

