Maturation of type I and type II rat vestibular hair cells in vivo and in vitro
- PMID: 38895157
- PMCID: PMC11183282
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1404894
Maturation of type I and type II rat vestibular hair cells in vivo and in vitro
Abstract
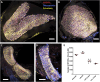
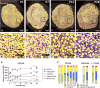
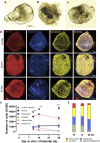
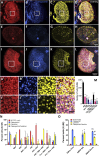
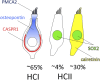
Vestibular sensory epithelia contain type I and type II sensory hair cells (HCI and HCII). Recent studies have revealed molecular markers for the identification of these cells, but the precise composition of each vestibular epithelium (saccule, utricle, lateral crista, anterior crista, posterior crista) and their postnatal maturation have not been described in detail. Moreover, in vitro methods to study this maturation are not well developed. We obtained total HCI and HCII counts in adult rats and studied the maturation of the epithelia from birth (P0) to postnatal day 28 (P28). Adult vestibular epithelia hair cells were found to comprise ∼65% HCI expressing osteopontin and PMCA2, ∼30% HCII expressing calretinin, and ∼4% HCII expressing SOX2 but neither osteopontin nor calretinin. At birth, immature HCs express both osteopontin and calretinin. P28 epithelia showed an almost adult-like composition but still contained 1.3% of immature HCs. In addition, we obtained free-floating 3D cultures of the epithelia at P1, which formed a fluid-filled cyst, and studied their survival and maturation in vitro up to day 28 (28 DIV). These cultures showed good HC resiliency and maturation. Using an enriched medium for the initial 4 days, a HCI/calretinin+-HCII ratio close to the in vivo ratio was obtained. These cultures are suitable to study HC maturation and mature HCs in pharmacological, toxicological and molecular research.
Keywords: 3D culture; SRY-box transcription factor 2 (SOX2); calretinin; contactin-associated protein 1 (CASPR1); osteopontin; plasma membrane calcium-transporting ATPase 2 (PMCA2); type I and type II hair cells; vestibular sensory hair cell.
Copyright © 2024 Borrajo, Sedano, Palou, Giménez-Esbrí, Barrallo-Gimeno and Llorens.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures


References
-
- Burns J. C., On D., Baker W., Collado M. S., Corwin J. T. (2012). Over half the hair cells in the mouse utricle first appear after birth, with significant numbers originating from early postnatal mitotic production in peripheral and striolar growth zones. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngology JARO 13 (5), 609–627. 10.1007/s10162-012-0337-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed

