Navigating the Intricacies of Tumor Heterogeneity: An Insight into Potential Prognostic Breast Cancer Biomarkers
- PMID: 38895160
- PMCID: PMC11185041
- DOI: 10.1177/11772719241256798
Navigating the Intricacies of Tumor Heterogeneity: An Insight into Potential Prognostic Breast Cancer Biomarkers
Abstract
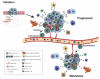
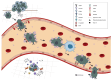
Breast cancer is a heterogeneous disease with diverse histological and molecular subtypes. Luminal breast tumors are the most diagnosed subtype. In luminal breast cancer, hormone receptors (including ER, PR, HER2) play a diagnostic and prognostic role. Despite the effectiveness of endocrine therapy in luminal breast tumors, tumor recurrence and resistance occur, and this may highlight evolutionary strategies for survival driven by stemness. In this review we thus consider the association between estrogen signaling and stemness in mediating tumor processes. Many studies report stemness as one of the factors promoting tumor progression. Its association with estrogen signaling warrants further investigation and provides an opportunity for the identification of novel biomarkers which may be used for diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic purposes. Breast cancer stem cells have been characterized (CD44+ CD24-) and their role in promoting treatment resistance and tumor recurrence widely studied; however, the complexity of tumor progression which also involve microenvironmental factors suggests the existence of more varied cell phenotypes which mediate stemness and its role in tumor progression.
Keywords: Breast cancer; estrogen; evolution; intratumoral heterogeneity; stemness.
© The Author(s) 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differences in stemness properties associated with the heterogeneity of luminal-type breast cancer.Clin Breast Cancer. 2015 Apr;15(2):e93-103. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2014.11.002. Epub 2014 Nov 10. Clin Breast Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25481840
-
Inhibition of Cdk2 kinase activity selectively targets the CD44⁺/CD24⁻/Low stem-like subpopulation and restores chemosensitivity of SUM149PT triple-negative breast cancer cells.Int J Oncol. 2014 Sep;45(3):1193-9. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2523. Epub 2014 Jun 25. Int J Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24970653 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic values of negative estrogen or progesterone receptor expression in patients with luminal B HER2-negative breast cancer.World J Surg Oncol. 2016 Sep 13;14(1):244. doi: 10.1186/s12957-016-0999-x. World J Surg Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27619909 Free PMC article.
-
Overview of resistance to systemic therapy in patients with breast cancer.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;608:1-22. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-74039-3_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17993229 Review.
-
Epigenetic Mechanisms of Tamoxifen Resistance in Luminal Breast Cancer.Diseases. 2017 Jul 6;5(3):16. doi: 10.3390/diseases5030016. Diseases. 2017. PMID: 28933369 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of the Microbiome and of Radiotherapy-Derived Metabolites in Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Oct 30;16(21):3671. doi: 10.3390/cancers16213671. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39518108 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209-249. - PubMed
-
- Finestone E, Wishnia J. Estimating the burden of cancer in South Africa. S Afr J Oncol. 2022;6:a220.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

