A review of MASLD-related hepatocellular carcinoma: progress in pathogenesis, early detection, and therapeutic interventions
- PMID: 38895182
- PMCID: PMC11184143
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1410668
A review of MASLD-related hepatocellular carcinoma: progress in pathogenesis, early detection, and therapeutic interventions
Abstract
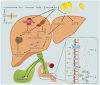
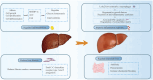
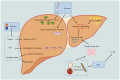
The incidence of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is continuously rising, evolving into a global health challenge. Concurrently, cases of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) associated with MASLD are also on the increase. Although traditional risk factors such as age, gender, and metabolic factors play significant roles in the development of HCC, it cannot be overlooked that MASLD, triggered by changes in modern lifestyle and dietary habits, may also exacerbate the risk of HCC, and this phenomenon is common even among non-obese individuals. Regrettably, MASLD often fails to receive timely diagnosis, resulting in a limited number of patients receiving HCC surveillance. Moreover, there is currently a lack of clear definition for the target population for surveillance beyond patients with cirrhosis. Consequently, MASLD-related HCC is often detected at a late stage, precluding the optimal timing for curative treatment. However, our understanding of the pathogenesis and progression of HCC remains limited. Therefore, this paper reviews relevant literature from recent years, delving into multiple dimensions such as pathogenesis, surveillance and diagnosis, prevention, and treatment, aiming to provide new ideas and directions for the prevention and treatment of MASLD-related HCC.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma; inflammatory response; metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; oxidative stress; the intestinal microbiome.
Copyright © 2024 Ma, Wang, Xiao and Fan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phenotypes of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Sep;22(9):1774-1789.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2024.03.028. Epub 2024 Apr 10. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38604295 Review.
-
MASLD-Related HCC: A Comprehensive Review of the Trends, Pathophysiology, Tumor Microenvironment, Surveillance, and Treatment Options.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Jun 13;46(6):5965-5983. doi: 10.3390/cimb46060356. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38921027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological therapy of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease-driven hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 19;14:1336216. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1336216. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38313077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Familial coaggregation of MASLD with hepatocellular carcinoma and adverse liver outcomes: Nationwide multigenerational cohort study.J Hepatol. 2023 Dec;79(6):1374-1384. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.08.018. Epub 2023 Aug 28. J Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 37647992
-
Lower hepatocellular carcinoma surveillance in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: Impact on treatment eligibility.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Dec;39(12):2817-2825. doi: 10.1111/jgh.16727. Epub 2024 Aug 27. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 39191435 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Metabolic syndrome is associated with worse prognosis in elderly patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2025 Apr 11;15:1542328. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1542328. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40291918 Free PMC article.
-
The Biological Clock of Liver Metabolism in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis Progression to Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Biomedicines. 2024 Aug 29;12(9):1961. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12091961. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39335475 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of a Novel four-gene Model for Monitoring the Progression from Metabolic Dysfunction-associated Steatotic Liver Disease to Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Males.J Cancer. 2025 Jan 1;16(3):917-931. doi: 10.7150/jca.100724. eCollection 2025. J Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39781352 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Analysis Revealed the Therapeutic Effect of Scutellarin on MASLD.ACS Omega. 2025 May 20;10(21):21095-21104. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c09465. eCollection 2025 Jun 3. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40488032 Free PMC article.
-
Intake of S-Methylmethionine Alters Glucose Metabolism and Hepatic Gene Expression in C57BL/6J High-Fat-Fed Mice.Foods. 2024 Dec 26;14(1):34. doi: 10.3390/foods14010034. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39796324 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

