Left atrial strain in neonates with congenital diaphragmatic hernia and length of stay in pediatric intensive care unit
- PMID: 38895191
- PMCID: PMC11183789
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2024.1404350
Left atrial strain in neonates with congenital diaphragmatic hernia and length of stay in pediatric intensive care unit
Abstract
Introduction: The role of cardiac left ventricle (LV) dysfunction in children with congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH) has gained increasing attention. The hernia allows abdominal mass to enter thorax and subsequently both dislocating and compressing the heart. The pressure on vessels and myocardium alters blood flow and may interfere with normal development of the LV. A dysfunctional LV is concerning and impacts the complex pathophysiology of CDH. Hence, assessing both the systolic and diastolic LV function in the newborn with CDH is important, and it may add value for medical treatment and prognostic factors as length of stay (LOS) in pediatric intensive care unit (PICU). LV strain is considered an early marker of systolic dysfunction used in the pediatric population. Left atrial (LA) strain is an echocardiographic marker of LV diastolic dysfunction used in the adult population. When filling pressure of the LV increases, the strain of the atrial wall is decreased. We hypothesized that reduced LA strain and LV strain are correlated with the LOS in the PICU of newborns with CDH.
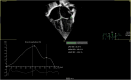
Methods: This retrospective observational cohort study included data of 55 children born with CDH between 2018 and 2020 and treated at Karolinska University Hospital, Sweden. Overall, 46 parents provided consent. Echocardiograms were performed in 35 children <72 h after birth. The LA reservoir strain (LASr), LV global longitudinal strain, LV dimensions, and direction of blood flow through the patent foramen ovale (PFO) were retrospectively assessed using the echocardiograms.
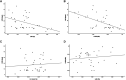
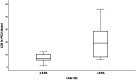
Results: Children with LASr <33% (n = 27) had longer stays in the PICU than children with LA strain ≥33% (n = 8) (mean: 20.8 vs. 8.6 days; p < 0.002). The LASr was correlated with the LOS in the PICU (correlation coefficient: -0.378; p = 0.025). The LV dimension was correlated with the LOS (correlation coefficient: -0.546; p = 0.01). However, LV strain was not correlated to LOS.
Conclusion: Newborns with CDH and a lower LASr (<33%) had longer stays in the PICU than children with LASr ≥33%. LASr is a feasible echocardiographic marker of diastolic LV dysfunction in newborns with CDH and may indicate the severity of the condition.
Keywords: CDH; cardiac function; congenital diaphragmatic hernia; diastolic function; left atrial strain; left ventricle strain; neonatal; systolic function.
© 2024 Tydén, Mesas Burgos, Jonsson and Nordenstam.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cardiac function in children with congenital diaphragmatic hernia: cardiac strain at birth and at 2-5 weeks of age.Front Pediatr. 2025 Jul 17;13:1598695. doi: 10.3389/fped.2025.1598695. eCollection 2025. Front Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40746355 Free PMC article.
-
Diminished Cardiac Performance and Left Ventricular Dimensions in Neonates with Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia.Pediatr Cardiol. 2018 Jun;39(5):993-1000. doi: 10.1007/s00246-018-1850-7. Epub 2018 Mar 9. Pediatr Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 29523920
-
Left atrial reservoir strain combined with E/E' as a better single measure to predict elevated LV filling pressures in patients with coronary artery disease.Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2020 Apr 25;18(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s12947-020-00192-4. Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2020. PMID: 32334586 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical aspects of left ventricular diastolic function assessed by Doppler echocardiography following acute myocardial infarction.Dan Med Bull. 2001 Nov;48(4):199-210. Dan Med Bull. 2001. PMID: 11767125 Review.
-
Left atrial strain evaluation to assess left ventricle diastolic dysfunction and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: a guide to clinical practice : Left atrial strain and diastolic function.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2023 Jun;39(6):1083-1096. doi: 10.1007/s10554-023-02816-y. Epub 2023 Feb 24. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2023. PMID: 36826616 Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiac function in children with congenital diaphragmatic hernia: cardiac strain at birth and at 2-5 weeks of age.Front Pediatr. 2025 Jul 17;13:1598695. doi: 10.3389/fped.2025.1598695. eCollection 2025. Front Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40746355 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

