This is a preprint.
Development of highly multiplex targeted proteomics assays in biofluids using the Stellar mass spectrometer
- PMID: 38895256
- PMCID: PMC11185584
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.06.04.597431
Development of highly multiplex targeted proteomics assays in biofluids using the Stellar mass spectrometer
Abstract
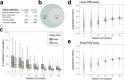
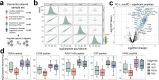
The development of targeted assays that monitor biomedically relevant proteins is an important step in bridging discovery experiments to large scale clinical studies. Targeted assays are currently unable to scale to hundreds or thousands of targets. We demonstrate the generation of large-scale assays using a novel hybrid nominal mass instrument. The scale of these assays is achievable with the Stellar™ mass spectrometer through the accommodation of shifting retention times by real-time alignment, while being sensitive and fast enough to handle many concurrent targets. Assays were constructed using precursor information from gas-phase fractionated (GPF) data-independent acquisition (DIA). We demonstrate the ability to schedule methods from an orbitrap and linear ion trap acquired GPF DIA library and compare the quantification of a matrix-matched calibration curve from orbitrap DIA and linear ion trap parallel reaction monitoring (PRM). Two applications of these proposed workflows are shown with a cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) neurodegenerative disease protein PRM assay and with a Mag-Net enriched plasma extracellular vesicle (EV) protein survey PRM assay.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The MacCoss Lab at the University of Washington has a sponsored research agreement with Thermo Fisher Scientific, the manufacturer of the mass spectrometry instrumentation used in this research. Additionally, MJM is a paid consultant for Thermo Fisher Scientific. PMR, CCJ, and LRH are employees of Thermo Fisher Scientific.
Figures




References
-
- Katz D. H.; Robbins J. M.; Deng S.; Tahir U. A.; Bick A. G.; Pampana A.; Yu Z.; Ngo D.; Benson M. D.; Chen Z.-Z.; Cruz D. E.; Shen D.; Gao Y.; Bouchard C.; Sarzynski M. A.; Correa A.; Natarajan P.; Wilson J. G.; Gerszten R. E. Proteomic Profiling Platforms Head to Head: Leveraging Genetics and Clinical Traits to Compare Aptamer- and Antibody-Based Methods. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8 (33), eabm5164. 10.1126/sciadv.abm5164. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ngo D.; Sinha S.; Shen D.; Kuhn E. W.; Keyes M. J.; Shi X.; Benson M. D.; O’Sullivan J. F.; Keshishian H.; Farrell L. A.; Fifer M. A.; Vasan R. S.; Sabatine M. S.; Larson M. G.; Carr S. A.; Wang T. J.; Gerszten R. E. Aptamer-Based Proteomic Profiling Reveals Novel Candidate Biomarkers and Pathways in Cardiovascular Disease. Circulation 2016, 134 (4), 270–285. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.021803. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Emilsson V.; Ilkov M.; Lamb J. R.; Finkel N.; Gudmundsson E. F.; Pitts R.; Hoover H.; Gudmundsdottir V.; Horman S. R.; Aspelund T.; Shu L.; Trifonov V.; Sigurdsson S.; Manolescu A.; Zhu J.; Olafsson Ö.; Jakobsdottir J.; Lesley S. A.; To J.; Zhang J.; Harris T. B.; Launer L. J.; Zhang B.; Eiriksdottir G.; Yang X.; Orth A. P.; Jennings L. L.; Gudnason V. Co-Regulatory Networks of Human Serum Proteins Link Genetics to Disease. Science 2018, 361 (6404), 769–773. 10.1126/science.aaq1327. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
