This is a preprint.
Medial amygdalar tau is associated with anxiety symptoms in preclinical Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 38895308
- PMCID: PMC11185761
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.06.03.597160
Medial amygdalar tau is associated with anxiety symptoms in preclinical Alzheimer's disease
Update in
-
Medial Amygdalar Tau Is Associated With Mood Symptoms in Preclinical Alzheimer's Disease.Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2024 Dec;9(12):1301-1311. doi: 10.1016/j.bpsc.2024.07.012. Epub 2024 Jul 25. Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2024. PMID: 39059466
Abstract
Background: While the amygdala receives early tau deposition in Alzheimer's disease (AD) and is involved in social and emotional processing, the relationship between amygdalar tau and early neuropsychiatric symptoms in AD is unknown. We sought to determine whether focal tau binding in the amygdala and abnormal amygdalar connectivity were detectable in a preclinical AD cohort and identify relationships between these and self-reported mood symptoms.
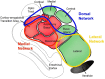
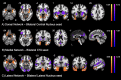
Methods: We examined n=598 individuals (n=347 amyloid-positive (58% female), n=251 amyloid-negative (62% female); subset into tau PET and fMRI cohorts) from the A4 Study. In our tau PET cohort, we used amygdalar segmentations to examine representative nuclei from three functional divisions of the amygdala. We analyzed between-group differences in division-specific tau binding in the amygdala in preclinical AD. We conducted seed-based functional connectivity analyses from each division in the fMRI cohort. Finally, we conducted exploratory post-hoc correlation analyses between neuroimaging biomarkers of interest and anxiety and depression scores.
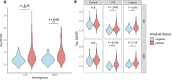
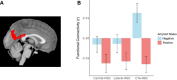
Results: Amyloid-positive individuals demonstrated increased tau binding in medial and lateral amygdala (F(4,442)=14.61, p=0.00045; F(4,442)=5.83, p=0.024, respectively). Across amygdalar divisions, amyloid-positive individuals had relatively increased regional connectivity from amygdala to other temporal regions, insula, and orbitofrontal cortex. There was an interaction by amyloid group between tau binding in the medial and lateral amygdala and anxiety. Medial amygdala to retrosplenial connectivity negatively correlated with anxiety symptoms (rs=-0.103, p=0.015).
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that preclinical tau deposition in the amygdala may result in meaningful changes in functional connectivity which may predispose patients to mood symptoms.
Keywords: amygdala; anxiety; default mode network; functional networks; preclinical Alzheimer’s disease; tau.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURES WX is currently employed in a fellowship role at Unlearn. AI Inc. JL, ST, BFT, SW, CH, TT, SN, CZ, YZ, AP, EB, and CF have no conflicts of interest or financial interests to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Benoit M, Dygai I, Migneco O, Robert PH, Bertogliati C, Darcourt J, et al. (1999): Behavioral and psychological symptoms in Alzheimer’s disease. Relation between apathy and regional cerebral perfusion. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 10: 511–7. - PubMed
-
- Kaufer DI, Cummings JL, Christine D, Bray T, Castellon S, Masterman D, et al. (1998): Assessing the impact of neuropsychiatric symptoms in Alzheimer’s disease: the Neuropsychiatric Inventory Caregiver Distress Scale. J Am Geriatr Soc 46: 210–215. - PubMed
-
- Johansson L, Guo X, Duberstein PR, Hallstrom T, Waern M, Ostling S, Skoog I (2014): Midlife personality and risk of Alzheimer disease and distress: a 38-year follow-up. Neurology 83: 1538–44. - PubMed
-
- Johansson M, Stomrud E, Lindberg O, Westman E, Johansson PM, van Westen D, et al. (2020): Apathy and anxiety are early markers of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiology of Aging 85: 74–82. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
