This is a preprint.
The protamines of the noble false widow spider Steatoda nobilis provide an example of liquid-liquid phase separation chromatin transitions during spermiogenesis
- PMID: 38895387
- PMCID: PMC11185589
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.06.04.597381
The protamines of the noble false widow spider Steatoda nobilis provide an example of liquid-liquid phase separation chromatin transitions during spermiogenesis
Update in
-
The protamines of the spider Steatoda sp. provide an example of liquid-liquid phase separation chromatin transitions during spermiogenesis.Development. 2024 Nov 15;151(22):dev203134. doi: 10.1242/dev.203134. Epub 2024 Nov 18. Development. 2024. PMID: 39465422 Free PMC article.
Abstract
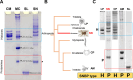
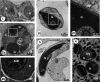
While there is extensive information about sperm nuclear basic proteins (SNBP) in vertebrates, there is very little information about Arthropoda by comparison. This paper aims to contribute to filling this gap by analyzing these proteins in the sperm of the noble false widow spider Steatoda nobilis (Order Araneae, Family Theridiidae). To this end, we have developed a protein extraction method that allows the extraction of cysteine-containing protamines suitable for the preparation and analysis of SNBPs from samples where the amount of starting tissue material is limited. We carried out top-down mass spectrometry sequencing and molecular phylogenetic analyses to characterize the protamines of S. nobilis and other spiders. We also used electron microscopy to analyze the chromatin organization of the sperm, and we found it to exhibit liquid-liquid phase spinodal decomposition during the late stages of spermiogenesis. These studies further our knowledge of the distribution of SNBPs within the animal kingdom and provide additional support for a proposed evolutionary origin of many protamines from a histone H1 (H5) replication-independent precursor.
Keywords: Sperm nuclear basic proteins (SNBPs); liquid-liquid phase separation; mass spectrometry; phylogeny; protamines; spider.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interest The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the study reported.
Figures


References
-
- Aiken D.E., Waddy S.L., Mercer S.M., 2004. Confirmation of External Fertilization in the American Lobster, Homarus Americanus. Journal of Crustacean Biology 24, 474–480.
-
- Ando T., Yamasaki M., and Suzuki K., 1973. Protamines: Isolation, Characterization and Function. Springer-Verlag, NY. - PubMed
-
- Arakawa K., Kono N., Malay A.D., Tateishi A., Ifuku N., Masunaga H., Sato R., Tsuchiya K., Ohtoshi R., Pedrazzoli D., Shinohara A., Ito Y., Nakamura H., Tanikawa A., Suzuki Y., Ichikawa T., Fujita S., Fujiwara M., Tomita M., Blamires S.J., Chuah J.A., Craig H., Foong C.P., Greco G., Guan J., Holland C., Kaplan D.L., Sudesh K., Mandal B.B., Norma-Rashid Y., Oktaviani N.A., Preda R.C., Pugno N.M., Rajkhowa R., Wang X., Yazawa K., Zheng Z., Numata K., 2022. 1000 spider silkomes: Linking sequences to silk physical properties. Sci Adv 8, eabo6043. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ausió J., 1992. Presence of a highly specific histone H1-like protein in the chromatin of the sperm of the bivalve mollusks. Mol Cell Biochem 115, 163–172. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
