This is a preprint.
AGS3-based optogenetic GDI induces GPCR-independent Gβγ signaling and macrophage migration
- PMID: 38895415
- PMCID: PMC11185739
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.06.04.597473
AGS3-based optogenetic GDI induces GPCR-independent Gβγ signaling and macrophage migration
Update in
-
AGS3-based optogenetic GDI induces GPCR-independent Gβγ signalling and macrophage migration.Open Biol. 2025 Feb;15(2):240181. doi: 10.1098/rsob.240181. Epub 2025 Feb 5. Open Biol. 2025. PMID: 39904370 Free PMC article.
Abstract
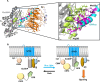
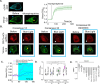
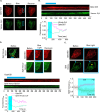
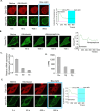
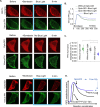
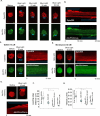
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are efficient Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) and exchange GDP to GTP on the Gα subunit of G protein heterotrimers in response to various extracellular stimuli, including neurotransmitters and light. GPCRs primarily broadcast signals through activated G proteins, GαGTP, and free Gβγ, and are major disease drivers. Evidence shows that the ambient low threshold signaling required for cells is likely supplemented by signaling regulators such as non-GPCR GEFs and Guanine nucleotide Dissociation Inhibitors (GDIs). Activators of G protein Signaling 3 (AGS3) are recognized as a GDI involved in multiple health and disease-related processes. Nevertheless, understanding of AGS3 is limited, and no significant information is available on its structure-function relationship or signaling regulation in living cells. Here, we employed in silico structure-guided engineering of a novel optogenetic GDI, based on the AGS3's G protein regulatory (GPR) motif, to understand its GDI activity and induce standalone Gβγ signaling in living cells on optical command. Our results demonstrate that plasma membrane recruitment of OptoGDI efficiently releases Gβγ, and its subcellular targeting generated localized PIP3 and triggered macrophage migration. Therefore, we propose OptoGDI as a powerful tool for optically dissecting GDI-mediated signaling pathways and triggering GPCR-independent Gβγ signaling in cells and in vivo.
Keywords: Activators of G protein Signaling 3; G proteins; GDI; GPCR; Macrophage migration; Optogenetics.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest concerning the contents of this article.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
