This is a preprint.
Unique trajectory of gene family evolution from genomic analysis of nearly all known species in an ancient yeast lineage
- PMID: 38895429
- PMCID: PMC11185758
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.06.05.597512
Unique trajectory of gene family evolution from genomic analysis of nearly all known species in an ancient yeast lineage
Update in
-
Unique trajectory of gene family evolution from genomic analysis of nearly all known species in an ancient yeast lineage.Mol Syst Biol. 2025 Aug;21(8):1066-1089. doi: 10.1038/s44320-025-00118-0. Epub 2025 May 27. Mol Syst Biol. 2025. PMID: 40425814 Free PMC article.
Abstract
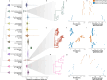
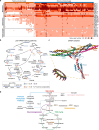
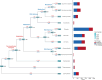
Gene gains and losses are a major driver of genome evolution; their precise characterization can provide insights into the origin and diversification of major lineages. Here, we examined gene family evolution of 1,154 genomes from nearly all known species in the medically and technologically important yeast subphylum Saccharomycotina. We found that yeast gene family and genome evolution are distinct from plants, animals, and filamentous ascomycetes and are characterized by small genome sizes and smaller gene numbers but larger gene family sizes. Faster-evolving lineages (FELs) in yeasts experienced significantly higher rates of gene losses-commensurate with a narrowing of metabolic niche breadth-but higher speciation rates than their slower-evolving sister lineages (SELs). Gene families most often lost are those involved in mRNA splicing, carbohydrate metabolism, and cell division and are likely associated with intron loss, metabolic breadth, and non-canonical cell cycle processes. Our results highlight the significant role of gene family contractions in the evolution of yeast metabolism, genome function, and speciation, and suggest that gene family evolutionary trajectories have differed markedly across major eukaryotic lineages.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests J.L.S. is an adviser for ForensisGroup, Inc. A.R. is a scientific consultant for LifeMine Therapeutics, Inc. The other authors declare no other competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Unique trajectory of gene family evolution from genomic analysis of nearly all known species in an ancient yeast lineage.Mol Syst Biol. 2025 Aug;21(8):1066-1089. doi: 10.1038/s44320-025-00118-0. Epub 2025 May 27. Mol Syst Biol. 2025. PMID: 40425814 Free PMC article.
-
Surveillance for Violent Deaths - National Violent Death Reporting System, 50 States, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico, 2022.MMWR Surveill Summ. 2025 Jun 12;74(5):1-42. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.ss7405a1. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2025. PMID: 40493548 Free PMC article.
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
