Reactivation Risk of Latent Tuberculosis or Inactive Hepatitis B Virus Infection and Effectiveness of Ustekinumab in Chinese Plaque Psoriasis Patients: A 28-Week Retrospective, Observational Study
- PMID: 38895605
- PMCID: PMC11185167
- DOI: 10.2147/CCID.S454971
Reactivation Risk of Latent Tuberculosis or Inactive Hepatitis B Virus Infection and Effectiveness of Ustekinumab in Chinese Plaque Psoriasis Patients: A 28-Week Retrospective, Observational Study
Abstract
Introduction: This study observed the effectiveness of ustekinumab and reactivation risk of concurrent latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) and inactive hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection in Chinese mainland psoriasis patients on ustekinumab treatment.
Methods: This retrospective, multicenter, observational study was conducted in three centers in China. Adult patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis were treated with ustekinumab for 28 weeks. The effectiveness endpoint included 75% and 90% improvement in Psoriasis Area Severity Index (PASI75/90) response rate, percentage of PASI improvement, change of absolute PASI score and body surface area involvement (BSA) score, absolute PASI ≤1/3 and Physicians' Global Assessment (PGA)=0/1, as well as Dermatology life quality index (DLQI)=0/1 response rate at week 4, 16 and 28. Screening of tuberculosis and hepatitis were performed at baseline and week 28.
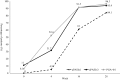
Results: A total of 82 patients were enrolled between March 2021 and May 2023 and the number of patients combined with LTBI and inactive HBV infection was 20 and 21 respectively. The PASI75 and PASI90 response rate at week 28 was 95.1% and 81.7% respectively. The mean PASI score decreased from 14.93 ± 12.07 at baseline to 0.78 ± 1.86 at week 28, and the mean BSA score decreased from 21% ± 18% at baseline to 1% ± 2% at week 28 (both P<0.001 compared with baseline). DLQI 0/1 response rate at week 28 was 73.2%. No reactivation of LTBI and inactive HBV infection and also no new-onset tuberculosis and hepatitis B occurred in patients without LTBI and inactive HBV infection at baseline.
Conclusion: Ustekinumab demonstrated great effectiveness in Chinese plaque psoriasis patients and good safety in psoriasis concurrent with LTBI and inactive HBV infection under the real-world setting.
Keywords: LTBI; inactive HBV infection; plaque psoriasis; real-world effectiveness; ustekinumab.
© 2024 Lu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest or financial disclosures that are pertinent to this article.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Real-life effectiveness and safety of guselkumab in patients with psoriasis who have an inadequate response to ustekinumab: A 104-week multicenter retrospective study - IL PSO (ITALIAN LANDSCAPE PSORIASIS).J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023 May;37(5):1017-1027. doi: 10.1111/jdv.18913. Epub 2023 Feb 8. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023. PMID: 36695061
-
Risk of Tuberculosis and Hepatitis B Reactivation in Patients With Crohn's Disease on Ustekinumab: A Nationwide Real-World Study.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2024 Jan 5;30(1):45-52. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izad032. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2024. PMID: 36880432
-
Efficacy and safety of ustekinumab in the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in Singapore.Singapore Med J. 2023 Jul;64(7):434-438. doi: 10.11622/smedj.2022029. Singapore Med J. 2023. PMID: 35196847 Free PMC article.
-
Ustekinumab: a review of its use in the management of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis.Drugs. 2011 Sep 10;71(13):1733-53. doi: 10.2165/11207530-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2011. PMID: 21902296 Review.
-
Ustekinumab.2020 Apr 20. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012–. 2020 Apr 20. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012–. PMID: 31643346 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Incidence of HBV Reactivation in Psoriasis Patients Undergoing Cytokine Inhibitor Therapy: A Single-Center Study and Systematic Review with a Meta-Analysis.Viruses. 2024 Dec 30;17(1):42. doi: 10.3390/v17010042. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39861831 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen XL, Zheng LY, Zhang H, et al. Disease burden and quality of life in patients with psoriasis: an internet-based questionnaire survey. Chin J Dermatol. 2019;52(11):791–795 doi:10.35541/cjd.20190247. - DOI
-
- Zhang XJ, Wang G, Zhang FR, Zhang XB, Li B. Guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of psoriasis in China (2023 edition). Chin J Dermatol. 2023;56(7):573–625 doi:10.35541/cjd.20220839. - DOI
-
- Bao CD, Chen YH, Gu JR, Gao MQ, Huang F. Expert position paper on tuberculosis prevention and management in tumor necrosis factor antagonist application. Chin J Rheumatol. 2013;17(8):508–512.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

