Ferroptosis: a new mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine for treating ulcerative colitis
- PMID: 38895617
- PMCID: PMC11184165
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1379058
Ferroptosis: a new mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine for treating ulcerative colitis
Abstract
Ulcerative colitis (UC), a subtype of inflammatory bowel disease, manifests with symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, and mucopurulent, bloody stools. The pathogenesis of UC is not fully understood. At present, the incidence of UC has increased significantly around the world. Conventional therapeutic arsenals are relatively limited, with often poor efficacy and many adverse effects. In contrast, traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) holds promise due to their notable effectiveness, reduced recurrence rates, and minimal side effects. In recent years, significant progress has been made in the basic research on TCM for UC treatment. It has been found that the inhibition of ferroptosis through the intervention of TCM can significantly promote intestinal mucosal healing and reverse UC. The mechanism of action involves multiple targets and pathways.
Aim of the review: This review summarizes the experimental studies on the targeted regulation of ferroptosis by TCM and its impact on UC in recent years, aiming to provide theoretical basis for the prevention, treatment, and further drug development for UC.
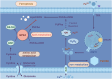
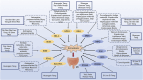
Results: Ferroptosis disrupts antioxidant mechanisms in intestinal epithelial cells, damages the intestinal mucosa, and participates in the pathological process of UC. TCM acts on various pathways such as Nrf2/HO-1 and GSH/GPX4, blocking the pathological progression of ferroptosis in intestinal epithelial cells, inhibiting pathological damage to the intestinal mucosa, and thereby alleviating UC.
Conclusion: The diverse array of TCM single herbs, extracts and herbal formulas facilitates selective and innovative research and development of new TCM methods for targeting UC treatment. Although progress has been made in studying TCM compound formulas, single herbs, and extracts, there are still many issues in clinical and basic experimental designs, necessitating further in-depth scientific exploration and research.
Keywords: Glutathion (GSH); ferroptosis; glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4); traditional Chinese medicine; ulcerative colitis.
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Hao, Yuan, Tian, Sun and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of ferroptosis: A new direction in the treatment of ulcerative colitis by traditional Chinese medicine.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Apr 24;324:117787. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.117787. Epub 2024 Jan 20. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38253272 Review.
-
Traditional Chinese Medicine: A promising strategy to regulate the imbalance of bacterial flora, impaired intestinal barrier and immune function attributed to ulcerative colitis through intestinal microecology.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Jan 10;318(Pt A):116879. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116879. Epub 2023 Jul 5. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37419224 Review.
-
Lizhong decoction ameliorates ulcerative colitis by inhibiting ferroptosis of enterocytes via the Nrf2/SLC7A11/GPX4 pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 May 23;326:117966. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.117966. Epub 2024 Feb 22. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38401661
-
A Comprehensive Review of Traditional Chinese Medicine in the Management of Ulcerative Colitis.Am J Chin Med. 2025;53(2):435-473. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X2550017X. Epub 2025 Mar 11. Am J Chin Med. 2025. PMID: 40066486 Review.
-
Potential activity of Traditional Chinese Medicine against Ulcerative colitis: A review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 May 10;289:115084. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115084. Epub 2022 Feb 5. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35134488 Review.
Cited by
-
Xuesanqi ameliorates DSS-induced colitis in mice by mediating gut microbiota dysbiosis and modulating MAPK/ERK/JNK pathway.Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2024 Dec 1;14(1):60. doi: 10.1007/s13659-024-00482-8. Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2024. PMID: 39616288 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal traditional Chinese medicine formulas in treating ulcerative colitis: Choose one or take it all?World J Clin Cases. 2024 Nov 16;12(32):6570-6574. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i32.6570. World J Clin Cases. 2024. PMID: 39554899 Free PMC article.
-
The biological roles of exosome-encapsulated traditional Chinese medicine monomers in neuronal disorders.J Pharm Anal. 2025 May;15(5):101131. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2024.101131. Epub 2024 Oct 28. J Pharm Anal. 2025. PMID: 40491425 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bengson E. F., Guggisberg C. A., Bastian T. W., Georgieff M. K., Ryu M. S. (2023). Quantitative omics analyses of NCOA4 deficiency reveal an integral role of ferritinophagy in iron homeostasis of hippocampal neuronal HT22 cells. Front. Nutr. 10, 1054852. 10.3389/fnut.2023.1054852 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials