Oligomeric amyloid-β targeted contrast agent for MRI evaluation of Alzheimer's disease mouse models
- PMID: 38895620
- PMCID: PMC11184063
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1392729
Oligomeric amyloid-β targeted contrast agent for MRI evaluation of Alzheimer's disease mouse models
Abstract
Background: Oligomeric amyloid beta (oAβ) is a toxic factor that acts in the early stage of Alzheimer's disease (AD) and may initiate the pathologic cascade. Therefore, detecting oAβ has a crucial role in the early diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment of AD.
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to evaluate MRI signal changes in different mouse models and the time-dependent signal changes using our novel gadolinium (Gd)-dodecane tetraacetic acid (DOTA)- ob5 aptamer contrast agent.
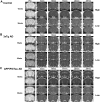
Methods: We developed an MRI contrast agent by conjugating Gd-DOTA-DNA aptamer called ob5 to evaluate its ability to detect oAβ deposits in the brain using MRI. A total of 10 control mice, 9 3xTg AD mice, and 11 APP/PS/Tau AD mice were included in this study, with the age of each model being 16 or 36 weeks. A T1-weighted image was acquired at the time points before (0 min) and after injection of the contrast agent at 5, 10, 15, 20, and 25 min. The analyses were performed to compare MRI signal differences among the three groups and the time-dependent signal differences in different mouse models.
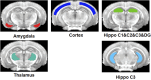
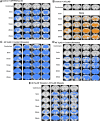
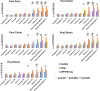
Results: Both 3xTg AD and APP/PS/Tau AD mouse models had higher signal enhancement than control mice at all scan-time points after injection of our contrast media, especially in bilateral hippocampal areas. In particular, all Tg AD mouse models aged 16 weeks showed a higher contrast enhancement than those aged 36 weeks. For 3xTg AD and APP/PS/Tau AD groups, the signal enhancement was significantly different among the five time points (0 min, 5 min, 10 min, 15 min, 20 min, and 25 min) in multiple ROI areas, typically in the bilateral hippocampus, left thalamus, and left amygdala.
Conclusion: The findings of this study suggest that the expression of the contrast agent in different AD models demonstrates its translational flexibility across different species. The signal enhancement peaked around 15-20 min after injection of the contrast agent. Therefore, our novel contrast agent targeting oAβ has the potential ability to diagnose early AD and monitor the progression of AD.
Keywords: ApoE mouse model; DNA aptamer; MRI contrast agent; oligomeric amyloid-beta; tau mouse model; time-dependent signal enhancement.
Copyright © 2024 Park, Tian, Kim, Park, Kim, Chung, Kim and Jahng.
Conflict of interest statement
S-TK and YK were employed by the J&Pharma. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

