miR‑146a‑5p protects against renal injury in MRL/lpr mice via improvement of the Treg/Th17 imbalance by targeting the TRAF6/NF‑κB axis
- PMID: 38895650
- PMCID: PMC11184638
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2022.11720
miR‑146a‑5p protects against renal injury in MRL/lpr mice via improvement of the Treg/Th17 imbalance by targeting the TRAF6/NF‑κB axis
Abstract
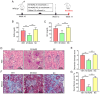
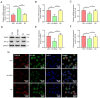
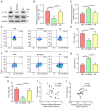
Dysregulated microRNA (miRNA or miR) expression is an important cause of immune homeostasis disorder in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis (LN). The present study evaluated the possibility of using miR-146a-5p as a therapeutic target for treating LN. The effects of miR-146a-5p on lupus syndrome in MRL/lpr mice were evaluated. MRL/lpr mice were injected with miR-146a-5p agomir (M146AG) or agomir negative control (NC). Renal function index, pathology and protein expression levels of inflammatory factors in MRL/lpr mice were evaluated after M146AG or agomir NC treatment. Reverse transcription-quantitative PCR, western blotting and immunofluorescence were used to assess the effect of M146AG on mRNA and protein expression levels of (tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6) TRAF6/NF-κB axis components. A luciferase dual reporter system was used to assess the mechanism of regulation of TRAF6/NF-κB axis expression. Finally, flow cytometry was used to assess the regulatory effect of M146AG on regulatory T cell (Treg)/T helper 17 (Th17) balance. The findings demonstrated that M146AG ameliorated renal lesions and the inflammatory response in MRL/lpr mice. TRAF6 was demonstrated to be targeted and significantly negatively regulated by miR-146a-5p. M146AG intervention significantly increased expression of miR-146a-5p and significantly downregulated the mRNA and protein expression levels of TRAF6 and NF-κB in CD4+ T cells of MRL/lpr mice. Furthermore, M146AG intervention alleviated Treg/Th17 imbalance in MRL/lpr mice peripheral blood. The present findings demonstrated that M146AG improved Treg/Th17 imbalance and alleviated renal lesions in MRL/lpr mice by targeting the TRAF6/NF-κB axis. This may provide a new theoretical basis for the clinical diagnosis and treatment of LN.
Keywords: NF-κB; TRAF6; Treg/Th17; lupus nephritis; miR-146a-5p.
Copyright: © 2020 Teng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
LncRNA PVT1 regulates CD4 + T cell dysregulation in systemic lupus erythematosus: insights from human patients and MRL/lpr mouse.Clin Rheumatol. 2025 Jul;44(7):2741-2750. doi: 10.1007/s10067-025-07519-4. Epub 2025 Jun 10. Clin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40493320 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-146a relieves kidney injury in mice with systemic lupus erythematosus through regulating NF-κB pathway.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Aug;23(16):7024-7032. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201908_18744. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31486503
-
Inhibition of microRNA-448 suppresses CD4+ T cell inflammatory activation via up-regulating suppressor of cytokine signaling 5 in systemic lupus erythematosus.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022 Mar 12;596:88-96. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.01.097. Epub 2022 Jan 29. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022. PMID: 35121374
-
Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell therapy ameliorates lupus through increasing CD4+ T cell senescence via MiR-199a-5p/Sirt1/p53 axis.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 1;11(2):893-905. doi: 10.7150/thno.48080. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33391511 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA miR-181d-5p regulates the MAPK signaling pathway by targeting mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 (MAPK8) to improve lupus nephritis.Gene. 2024 Jan 30;893:147961. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2023.147961. Epub 2023 Nov 4. Gene. 2024. PMID: 37931853
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
