The Diagnosis and Treatment of Tricuspid Regurgitation
- PMID: 38895810
- PMCID: PMC11551545
- DOI: 10.3238/arztebl.m2024.0104
The Diagnosis and Treatment of Tricuspid Regurgitation
Abstract
Background: It is estimated that 6% of persons over age 75 have clinically relevant tricuspid regurgitation (TR). This condition carries a high mortality and is of particular interest because of the recent development of new interventional treatments.
Methods: This review is based on publications that were retrieved by a selective search in the PubMed database for randomized controlled trials (RCTs), observational studies, registry studies, expert recommendations, and current international guidelines.
Results: The evidence reveals that TR is an independent cause of mortality. Mortality is correlated with the severity of TR: approximately 35% of patients with severe TR and right heart failure die within 1 year, and about 60% within 3 years. The clinical course varies depending on the etiology (primary TR, atrial/ventricular secondary TR, association with pacemaker systems). In the outpatient setting, timely diagnosis by transthoracic echocardiography is crucial. The options for pharmacotherapy are essentially limited to diuretic treatment (grade 2a recommendation). Early referral to a specialized heart valve center is essential for the prevention of irreversible damage of the right heart and secondary end-organ damage, including cardiohepatic and cardiorenal syndromes. In the heart valve center, an extended diagnostic evaluation with multimodal imaging is followed by a case discussion by the interdisciplinary cardiac team, with individual evaluation of the treatment options. The first randomized controlled trial of treatment for TR yielded a win ratio of 1.48 (95% confidence interval, [1.06; 2.13]) for interventional treatment (edge-to-edge repair) compared to optimal medical therapy.
Conclusion: As the understanding of tricuspid regurgitation improves, strategies for its interventional treatment are undergoing steady development, with the aim of lowering the mortality of this condition.
Figures

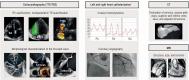
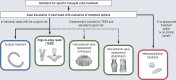

References
-
- Topilsky Y, Maltais S, Medina Inojosa J, et al. Burden of tricuspid regurgitation in patients diagnosed in the community setting. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019;12:433–442. - PubMed
-
- Cahill TJ, Prothero A, Wilson J, et al. Community prevalence, mechanisms and outcome of mi+6tral or tricuspid regurgitation. Heart. 2021;107:1003–1009. - PubMed
-
- Offen S, Playford D, Strange G, Stewart S, Celermajer DS. Adverse prognostic impact of even mild or moderate tricuspid regurgitation: insights from the National Echocardiography Database of Australia. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2022;35:810–817. - PubMed
-
- Kadri AN, Menon V, Sammour YM, et al. Outcomes of patients with severe tricuspid regurgitation and congestive heart failure. Heart. 2019;105:1813–1817. - PubMed
-
- Taramasso M, Benfari G, van der Bijl P, et al. Transcatheter versus medical treatment of patients with symptomatic severe tricuspid regurgitation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74:2998–3008. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

