Potential role of blood pressure variability and plasma neurofilament light in the mechanism of comorbidity between Alzheimer's disease and cerebral small vessel disease
- PMID: 38895921
- PMCID: PMC11247680
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.14056
Potential role of blood pressure variability and plasma neurofilament light in the mechanism of comorbidity between Alzheimer's disease and cerebral small vessel disease
Abstract
Introduction: Long-term blood pressure variability (BPV) and plasma neurofilament light (pNfL) have been identified as potential biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease (AD) and cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD). However, the relationship between BPV, pNfL, and their association with the comorbidity of AD and CSVD remains unknown.
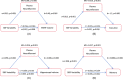
Methods: Participants with normal cognition and mild cognitive impairment from the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative study were included in the data analysis. Linear mixed-effects regression models and causal mediation analyses were conducted to investigate the relationship among BPV, pNfL, comorbidity-related brain structural changes (hippocampal atrophy and white matter hyperintensities [WMH]), and cognitive function.
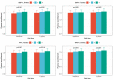
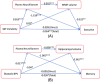
Results: BPV was associated with pNfL, volumes of hippocampus and WMH, and cognition. pNfL mediated the effects of BPV on brain structural changes and cognition.
Discussion: Our findings suggest a potential role of BPV and pNfL in the mechanism of comorbidity between AD and CSVD, underscoring the importance of BPV intervention in the general population.
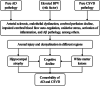
Highlights: Individuals with both Alzheimer's disease (AD) and cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD) pathologies had elevated blood pressure variability (BPV) and plasma neurofilament light (pNfL). The association between different components of BPV and brain structural changes may vary. BPV was associated with pNfL levels independent of average blood pressure. pNfL mediated the effects of BPV on comorbidity-related brain structural changes and cognitive performance.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; biomarker; blood pressure variability; cerebral small vessel disease; neurofilament light.
© 2024 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. Author disclosures are available in the supporting information.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Utility of Plasma Neurofilament Light in the 1Florida Alzheimer's Disease Research Center (ADRC).J Alzheimers Dis. 2021;79(1):59-70. doi: 10.3233/JAD-200901. J Alzheimers Dis. 2021. PMID: 33216030 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of Plasma Neurofilament Light Chain and Mini-Mental State Examination Score Predicts Progression from Mild Cognitive Impairment to Alzheimer's Disease within 5 Years.J Alzheimers Dis. 2021;82(3):951-964. doi: 10.3233/JAD-210092. J Alzheimers Dis. 2021. PMID: 34120902
-
The polygenic hazard score mediates the association between plasma neurofilament light chain and brain morphometry in dementia spectrum.Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2025 Mar;130:105703. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2024.105703. Epub 2024 Nov 25. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2025. PMID: 39631103
-
Association Between Blood Pressure Variability and Cerebral Small-Vessel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Am Heart Assoc. 2020 Jan 7;9(1):e013841. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.013841. Epub 2019 Dec 24. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020. PMID: 31870233 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma neuronal exosomes serve as biomarkers of cognitive impairment in HIV infection and Alzheimer's disease.J Neurovirol. 2019 Oct;25(5):702-709. doi: 10.1007/s13365-018-0695-4. Epub 2019 Jan 4. J Neurovirol. 2019. PMID: 30610738 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- cstc2019jcyj-zdxmX0029/Chongqing Natural Science Fund Key Project
- GE Healthcare
- Kuanren Talents Program of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University
- AbbVie
- Transition Therapeutics
- Cogstate
- Eisai Inc.
- W81XWH-12-2-0012/Department of Defense
- EuroImmun
- Biogen
- CSTB2023NSCQ-MSX0198/Chongqing Natural Science Fund General Program
- Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative
- Alzheimer's Drug Discovery Foundation
- Servier
- Lumosity
- Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
- U01 AG024904/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- Piramal Imaging
- Takeda Pharmaceutical Company
- ALZ/Alzheimer's Association/United States
- Genentech, Inc.
- Araclon Biotech
- U01 AG024904/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- Meso Scale Diagnostics, LLC
- Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation
- CereSpir, Inc.
- BioClinica, Inc.
- EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceutical Research & Development LLC
- Pfizer Inc.
- Elan Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
- Eli Lilly and Company
- IXICO Ltd.
- NeuroRx Research
- Merck & Co., Inc.
- Janssen Alzheimer Immunotherapy Research & Development, LLC
- Neurotrack Technologies
- Fujirebio
- Lundbeck
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

