How does robotic surgery affect gynecology patient care?
- PMID: 38896293
- PMCID: PMC11186900
- DOI: 10.1007/s11701-024-01955-1
How does robotic surgery affect gynecology patient care?
Abstract
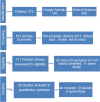
The aim of this review is to map the current research on the needs of gynecological patients treated with robotic surgery. Systematic Rapid Review. Pubmed, Web of Science, Google Scholar. Search was limited from the years 2017-2021. The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) statement was followed. Rapid review is a synthesis of information produced in a shorter time than systematic reviews, which allows clinical nurses to access evidence in the decision-making process. The methodological steps implemented were the following: (1) needs assessment and topic selection, (2) study development, (3) literature search, (4) screening and study selection, (5) data extraction, (6) risk-of-bias assessment and (7) knowledge synthesis. The search yielded 815 articles, 746 were excluded after screening the title and abstract, and 69 full-text syntheses were performed. Only 10 articles were included in the final analysis. This research evaluated the effects of robotic surgery on the patient under seven themes; operative time, length of stay, complications, estimated blood loss, pain, survivor, and conversion. Five studies were on endometrial cancer, one study on gynecologic cancer, two studies on hysterectomy, one study on patient safety, and one study on cervical cancer. The results show that robotic surgery can change the needs of patients by solving ongoing problems in gynecological patients. This requires a better understanding of robotic surgery procedures while facilitating nursing care over patient care.
Keywords: Gynecological robotic surgery; Patient need; Robotic surgery; Robotic surgery nursing.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest between the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Vigo F, Egg R, Schoetzau A, Montavon C, Brezak M, Heinzelmann-Schwarz V, Kavvadias T (2022) An interdisciplinary team-training protocol for robotic gynecologic surgery improves operating time and costs: analysis of a 4-year experience in a university hospital setting. J Robot Surg 16:89–96. 10.1007/s11701-021-01209-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Saini S, Orlando MF, Pathak PM (2022) Intelligent control of a master-slave based robotic surgical system. J Intell Rob Syst 105(4):2–20. 10.1007/s10846-022-01684-3 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources