Clinical practice enhanced by interdisciplinary theoretical perspectives
- PMID: 38896442
- PMCID: PMC11552296
- DOI: 10.1080/02813432.2024.2368852
Clinical practice enhanced by interdisciplinary theoretical perspectives
Abstract
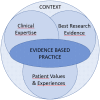
Background: Experience-based knowing in general practice includes advanced interpretation of subjective, complex and particular phenomena in a social context. Enabling different metapositions for reflexivity may provide the accountability needed for such knowing to be recognized as evidence-based practice.
Objective: To demonstrate and discuss the potential of substantive theories to enhance interpretation of complex challenges in clinical knowing in general practice.
Methods: We present a fictional case to demonstrate how interdisciplinary substantive theories, with a relevant and specific match to concrete questions, can situate the clinical interaction at an accountable platform. A female patient with Parkinson's disease consults her GP complaining that the disease is restraining her life and threatening her future. The GP has some new ideas from Bandura's theory of self-efficacy and introduces the patient to strategies for further action.
Findings: The case presents an example of how a relevant substantive theory may offer the GP: 1) a sharper focus for achievement: recognising the issues of fear and identity in chronic, progressive illness, 2) a subsequent position for individualized understanding of adequate strategies: encouraging physical and social activity in a well-known context, and 3) an invitation to consider further possibilities: finding ways to alleviate the burden of fear and progressive decline; engaging in joyful living.
Implications: General practice knowledge embraces a diversity of sources with different evidence power. The transparency mediated to clinical practice when supported by relevant substantive theories may contribute to recognition of experience-based knowing as evidence-based practice.
Keywords: Clinical medicine; evidence-based practice; experience-based knowledge; general practice; interdisciplinary theories.
Plain language summary
Experience-based knowing is an important capacity for interpretation of complex phenomena in general practice, but support for elaboration and analysis of such strategies is limitedInterdisciplinary substantive theories can enable reflexivity and enhance clinical practiceSubstantive theories may offer sharper focus, individualised understanding and recognition of additional possibilitiesA connection to specific theoretical ideas may augment the transparency of experience-based knowing, thus advancing attitudes for evidence-based practice.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report there are no competing interests to declare
Figures
References
-
- McWhinney IR. An acquaintance with particulars…. Fam Med. 1989;21(4):296–298. - PubMed
-
- Lonergan BHR . Insight. In: A study of human understanding. Toronto: University of Toronto Press; 1992.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical