QUALITY OF LIFE USING EURAHS-QoL SCORES AFTER SURGICAL TREATMENT OF INGUINAL HERNIA: LAPAROSCOPIC TRANSABDOMINAL PREPERITONEAL (TAPP) AND LICHTENSTEIN TECHNIQUES
- PMID: 38896698
- PMCID: PMC11182626
- DOI: 10.1590/0102-672020240005e1798
QUALITY OF LIFE USING EURAHS-QoL SCORES AFTER SURGICAL TREATMENT OF INGUINAL HERNIA: LAPAROSCOPIC TRANSABDOMINAL PREPERITONEAL (TAPP) AND LICHTENSTEIN TECHNIQUES
Abstract
Background: Results on quality of life after inguinal hernia surgery, such as esthetics, postoperative pain, period of absence from activities, and recurrence are a relevant topic since inguinal hernia affects 27% of men and 3% of women at some point in their lives, and should guide health policies to allocate resources more efficiently.
Aims: To evaluate the quality of life in the late postoperative period of inguinal herniorrhaphy regarding recurrence, pain, esthetics, and restriction in activities, comparing the minimally invasive techniques - the transabdominal preperitoneal (TAPP) and the conventional Lichtenstein.
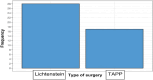
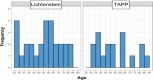
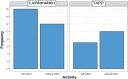
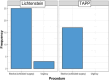
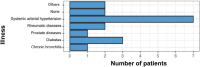
Methods: A cross-sectional observational clinical study was conducted with the EuraHS-QoL questionnaire validated and translated into Portuguese, applied to patients after an average of 65 months postoperatively. Forty-five patients were assessed, 28 undergoing Lichtenstein and 17 undergoing TAPP. All were males aged between 18 and 87 years with a primary unilateral inguinal hernia. Recurrent or bilateral hernias, other concomitant abdominal wall hernias, patients who chose not to participate or who were not found, and female patients were excluded from the study.
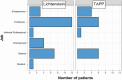
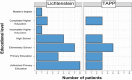
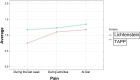
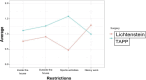
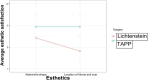
Results: Regarding the domains pain, restriction, and esthetics, there was no difference between the two groups when examining quality of life. Neither group presented recurrence in the studied period.
Conclusions: Both TAPP and Lichtenstein techniques presented similar results concerning quality of life when compared in the long-term.
RACIONAL:: Os resultados de qualidade de vida após cirurgia de hérnia inguinal, como estética, dor pós-operatória, período de afastamento das atividades e recorrência é um tema relevante, uma vez que a hérnia inguinal atinge 27% dos homens e 3% das mulheres em algum momento da vida, e deveriam orientar as políticas de saúde para alocar recursos de forma mais eficiente.
OBJETIVOS:: Avaliar a qualidade de vida no pós-operatório tardio de herniorrafia inguinal quanto a recidiva, dor, estética e restrição de atividades, comparando as técnicas minimamente invasivas transabdominal pré-peritoneal (TAPP) e convencional, Lichtenstein.
MÉTODOS:: Estudo clínico observacional transversal com questionário EuraHS-QoL validado e traduzido para o português, aplicado em pacientes após média de 65 meses de pós-operatório. Foram estudados 45 pacientes, 28 submetidos a Lichtenstein e 17 submetidos a TAPP. Todos eram do sexo masculino, com idade entre 18 e 87 anos, com hérnia inguinal unilateral primária. Hérnias recorrentes ou bilaterais, outras hérnias concomitantes da parede abdominal, pacientes que optaram por não participar ou que não foram encontrados e pacientes do sexo feminino foram excluídos do estudo.
RESULTADOS:: Em relação aos domínios dor, restrição e cosméticos, não houve diferença entre os dois grupos na avaliação da qualidade de vida. Os dois grupos não apresentaram recidiva no período estudado.
CONCLUSÕES:: Tanto a técnica TAPP quanto a técnica de Lichtenstein, neste estudo, apresentaram resultados semelhantes, quando comparadas em longo prazo, no que diz respeito à qualidade de vida
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Bilateral inguinal hernia repair and male fertility: a randomized clinical trial comparing Lichtenstein versus laparoscopic transabdominal preperitoneal (TAPP) technique.Surg Endosc. 2023 Dec;37(12):9263-9274. doi: 10.1007/s00464-023-10499-8. Epub 2023 Oct 25. Surg Endosc. 2023. PMID: 37880447 Clinical Trial.
-
A Comparison of Outcomes between Lichtenstein and Laparoscopic Transabdominal Preperitoneal Hernioplasty for Recurrent Inguinal Hernia.Am Surg. 2018 Nov 1;84(11):1774-1780. Am Surg. 2018. PMID: 30747632 Clinical Trial.
-
A prospective, randomized comparison of long-term outcomes: chronic groin pain and quality of life following totally extraperitoneal (TEP) and transabdominal preperitoneal (TAPP) laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair.Surg Endosc. 2013 Jul;27(7):2373-82. doi: 10.1007/s00464-013-2797-7. Epub 2013 Feb 7. Surg Endosc. 2013. PMID: 23389072 Clinical Trial.
-
Primary unilateral not complicated inguinal hernia: our choice of TAPP, why, results and review of literature.Hernia. 2019 Jun;23(3):417-428. doi: 10.1007/s10029-019-01959-z. Epub 2019 May 8. Hernia. 2019. PMID: 31069580
-
Meta-analysis and review of prospective randomized trials comparing laparoscopic and Lichtenstein techniques in recurrent inguinal hernia repair.Hernia. 2015 Jun;19(3):355-66. doi: 10.1007/s10029-014-1281-1. Epub 2014 Jul 18. Hernia. 2015. PMID: 25033943 Review.
References
-
- Amid PK, Shulman AG, Lichtenstein IL. Open “tension-free” repair of inguinal hernias: the Lichtenstein technique. Eur J Surg. 1996;162(6):447–53. - PubMed
-
- Azevedo MA, Oliveira GBT, Malheiros CA, Roll S. Are there differences in chronic pain after laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair using the transabdominal technique comparing with fixation of the mesh with staples, with glue or without fixation? A clinical randomized, double-blind trial. Arq Bras Cir Dig. 2022;35:e1670. doi: 10.1590/0102-672020220002e1670. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

