Preoperative prediction of renal fibrous capsule invasion in clear cell renal cell carcinoma using CT-based radiomics model
- PMID: 38897659
- PMCID: PMC11332665
- DOI: 10.1093/bjr/tqae122
Preoperative prediction of renal fibrous capsule invasion in clear cell renal cell carcinoma using CT-based radiomics model
Abstract
Objectives: To develop radiomics-based classifiers for preoperative prediction of fibrous capsule invasion in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) patients by CT images.
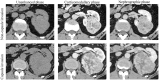
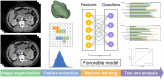
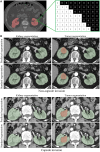
Methods: In this study, clear cell RCC (ccRCC) patients who underwent both preoperative abdominal contrast-enhanced CT and nephrectomy surgery at our hospital were analysed. By transfer learning, we used base model obtained from Kidney Tumour Segmentation challenge dataset to semi-automatically segment kidney and tumours from corticomedullary phase (CMP) CT images. Dice similarity coefficient (DSC) was measured to evaluate the performance of segmentation models. Ten machine learning classifiers were compared in our study. Performance of the models was assessed by their accuracy, precision, recall, and area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC). The reporting and methodological quality of our study was assessed by the CLEAR checklist and METRICS score.
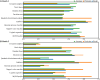
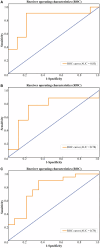
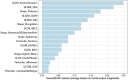
Results: This retrospective study enrolled 163 ccRCC patients. The semiautomatic segmentation model using CMP CT images obtained DSCs of 0.98 in the training cohort and 0.96 in the test cohort for kidney segmentation, and DSCs of 0.94 and 0.86 for tumour segmentation in the training and test set, respectively. For preoperative prediction of renal capsule invasion, the AdaBoost had the best performance in batch 1, with accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score equal to 0.8571, 0.8333, 0.9091, and 0.8696, respectively; and the same classifier was also the most suitable for this classification in batch 2. The AUCs of AdaBoost for batch 1 and batch 2 were 0.83 (95% CI: 0.68-0.98) and 0.74 (95% CI: 0.51-0.97), respectively. Nine common significant features for classification were found from 2 independent batch datasets, including morphological and texture features.
Conclusions: The CT-based radiomics classifiers performed well for the preoperative prediction of fibrous capsule invasion in ccRCC.
Advances in knowledge: Noninvasive prediction of renal fibrous capsule invasion in RCC is rather difficult by abdominal CT images before surgery. A machine learning classifier integrated with radiomics features shows a promising potential to assist surgical treatment options for RCC patients.
Keywords: CT; clear cell renal cell carcinoma; radiomics; renal fibrous capsule invasion.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Institute of Radiology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394-424. - PubMed
-
- Amin MB, Edge SB, Greene FL, Byrd DR, Brookland RK, Washington MK, et al. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. In: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 8th ed. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2017.
-
- Mir MC, Derweesh I, Porpiglia F, Zargar H, Mottrie A, Autorino R. Partial nephrectomy versus radical nephrectomy for clinical T1b and T2 renal tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative studies. Eur Urol. 2017;71(4):606-617. - PubMed

