Ultrasound of the forefeet besides the hands in patients at risk for rheumatoid arthritis: is it worth the effort? A longitudinal cohort study
- PMID: 38897668
- PMCID: PMC11962884
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keae339
Ultrasound of the forefeet besides the hands in patients at risk for rheumatoid arthritis: is it worth the effort? A longitudinal cohort study
Abstract
Objective: US can detect subclinical joint-inflammation in patients with clinically suspect arthralgia (CSA), which is valuable as predictor for RA development. In most research protocols both hands and forefeet are scanned, but it is unclear if US of the forefeet has additional value for predicting RA, especially since synovial hypertrophy in MTP-joints of healthy individuals is also common. To explore the possibility to omit scanning of the forefeet we determined if US of the forefeet is of additional predictive value for RA-development in CSA patients.
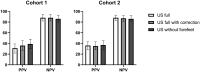
Methods: CSA patients of two independent cohorts underwent US of the hands and forefeet. We analysed the association between RA-development and US-positivity for the full US-protocol, the full US-protocol with correction for gray scale (GS)-findings in the forefeet of healthy and the protocol without forefeet.
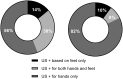
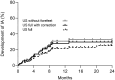
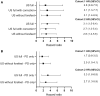
Results: In total, 298 CSA patients were studied. In patients with a positive US, subclinical joint-inflammation was mostly present in the hands (90-86%). Only 10-14% of patients had subclinical joint-inflammation solely in the forefeet. US-positivity was associated with inflammatory arthritis development in both cohorts, with HRs 2.6 (95% CI 0.9-7.5) and 3.1 (95% CI 1.5-6.4) for the full protocol, 3.1 (95% CI 1.3-7.7) and 2.7 (95% CI 1.3-5.4) for the full US-protocol with correction, and 3.1 (95% CI 1.4-6.9) and 2.8 (95% CI 1.4-5.6) without the forefeet. AUROCs were equal across both cohorts.
Conclusion: The forefeet can be omitted when US is used for the prediction of RA-development in CSA patients. This is due to the finding that subclinical joint-inflammation in the forefeet without concomitant inflammation in the hands is infrequent.
Keywords: diagnostic imaging; foot; observational studies; rheumatoid arthritis; ultrasonography.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Patient-reported swelling in arthralgia patients at risk for rheumatoid arthritis: is it of value?Rheumatology (Oxford). 2024 Dec 1;63(12):3415-3421. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kead606. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2024. PMID: 37952171 Free PMC article.
-
Improving the feasibility of MRI in clinically suspect arthralgia for prediction of rheumatoid arthritis by omitting scanning of the feet.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020 Jun 1;59(6):1247-1252. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kez436. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020. PMID: 31566238 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic value of magnetic resonance imaging of the forefeet in early rheumatoid arthritis when findings on imaging of the metacarpophalangeal joints of the hands remain normal.Arthritis Rheum. 2004 Jul;50(7):2094-102. doi: 10.1002/art.20314. Arthritis Rheum. 2004. PMID: 15248206
-
What is the value of musculoskeletal ultrasound in patients presenting with arthralgia to predict inflammatory arthritis development? A systematic literature review.Arthritis Res Ther. 2018 Oct 11;20(1):228. doi: 10.1186/s13075-018-1715-8. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 30305156 Free PMC article.
-
Conventional radiography of the hands and wrists in rheumatoid arthritis. What a rheumatologist should know and how to interpret the radiological findings.Rheumatol Int. 2019 Aug;39(8):1331-1341. doi: 10.1007/s00296-019-04326-4. Epub 2019 May 22. Rheumatol Int. 2019. PMID: 31119369 Review.
Cited by
-
Ultrasound Predictors for Persistence or a Change in the Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis After 5 Years-A Prospective Cohort Study of Patients with Early Rheumatoid Arthritis.Biomedicines. 2025 May 19;13(5):1226. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13051226. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40427053 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zufferey P, Rebell C, Benaim C. et al. Ultrasound can be useful to predict an evolution towards rheumatoid arthritis in patients with inflammatory polyarthralgia without anticitrullinated antibodies. Joint Bone Spine 2017;84:299–303. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

