Genetic analysis based on next generation sequencing of Streptococcus equi subsp. equi isolated from horses imported into Japan
- PMID: 38897953
- PMCID: PMC11300130
- DOI: 10.1292/jvms.23-0342
Genetic analysis based on next generation sequencing of Streptococcus equi subsp. equi isolated from horses imported into Japan
Abstract
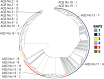
Strangles is a globally widespread, commonly diagnosed and important infectious disease of equids caused by Streptococcus equi subsp. equi. We performed whole genome sequencing of 19 S. equi isolates collected from imported horses at the Japanese border. Of these isolates, 15 isolates were obtained from clinical cases and 4 were from subclinical cases. The 19 isolates were grouped into 3 Bayesian analysis of population structure (BAPS) groups by the core genome single nucleotide polymorphism analysis corresponding to exporting country, SeM typing, or exporter of the horses. The 19 isolates possessed same pathogenic genes regardless of clinical status in imported horses and no antimicrobial resistance genes. The disease status of the horses may rather reflect the prior exposure of animals with sub-clinical infection to S. equi.
Keywords: Streptococcus equi; animal quarantine service; genetic analysis; next generation sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Anzai T, Kuwamoto Y, Wada R, Sugita S, Kakuda T, Takai S, Higuchi T, Timoney JF. 2005. Variation in the N-terminal region of an M-like protein of Streptococcus equi and evaluation of its potential as a tool in epidemiologic studies. Am J Vet Res 66: 2167–2171. doi: 10.2460/ajvr.2005.66.2167 - DOI - PubMed

