Exosomal miR-17-5p derived from epithelial cells is involved in aberrant epithelium-fibroblast crosstalk and induces the development of oral submucosal fibrosis
- PMID: 38897993
- PMCID: PMC11187069
- DOI: 10.1038/s41368-024-00302-2
Exosomal miR-17-5p derived from epithelial cells is involved in aberrant epithelium-fibroblast crosstalk and induces the development of oral submucosal fibrosis
Abstract
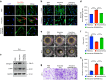
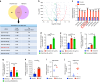
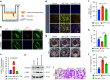
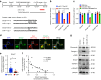
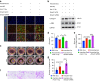
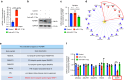
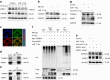
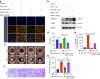
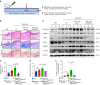
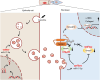
Oral submucous fibrosis (OSF) is a chronic and inflammatory mucosal disease caused by betel quid chewing, which belongs to oral potentially malignant disorders. Abnormal fibroblast differentiation leading to disordered collagen metabolism is the core process underlying OSF development. The epithelium, which is the first line of defense against the external environment, can convert external signals into pathological signals and participate in the remodeling of the fibrotic microenvironment. However, the specific mechanisms by which the epithelium drives fibroblast differentiation remain unclear. In this study, we found that Arecoline-exposed epithelium communicated with the fibrotic microenvironment by secreting exosomes. MiR-17-5p was encapsulated in epithelial cell-derived exosomes and absorbed by fibroblasts, where it promoted cell secretion, contraction, migration and fibrogenic marker (α-SMA and collagen type I) expression. The underlying molecular mechanism involved miR-17-5p targeting Smad7 and suppressing the degradation of TGF-β receptor 1 (TGFBR1) through the E3 ubiquitination ligase WWP1, thus facilitating downstream TGF-β pathway signaling. Treatment of fibroblasts with an inhibitor of miR-17-5p reversed the contraction and migration phenotypes induced by epithelial-derived exosomes. Exosomal miR-17-5p was confirmed to function as a key regulator of the phenotypic transformation of fibroblasts. In conclusion, we demonstrated that Arecoline triggers aberrant epithelium-fibroblast crosstalk and identified that epithelial cell-derived miR-17-5p mediates fibroblast differentiation through the classical TGF-β fibrotic pathway, which provided a new perspective and strategy for the diagnosis and treatment of OSF.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

