Epigenetic signature of very low birth weight in young adult life
- PMID: 38898107
- PMCID: PMC11798856
- DOI: 10.1038/s41390-024-03354-6
Epigenetic signature of very low birth weight in young adult life
Abstract
Background: Globally, one in ten babies is born preterm (<37 weeks), and 1-2% preterm at very low birth weight (VLBW, <1500 g). As adults, they are at increased risk for a plethora of health conditions, e.g., cardiometabolic disease, which may partly be mediated by epigenetic regulation. We compared blood DNA methylation between young adults born at VLBW and controls.
Methods: 157 subjects born at VLBW and 161 controls born at term, from the Helsinki Study of Very Low Birth Weight Adults, were assessed for peripheral venous blood DNA methylation levels at mean age of 22 years. Significant CpG-sites (5'-C-phosphate-G-3') were meta-analyzed against continuous birth weight in four independent cohorts (pooled n = 2235) with cohort mean ages varying from 0 to 31 years.
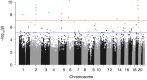
Results: In the discovery cohort, 66 CpG-sites were differentially methylated between VLBW adults and controls. Top hits were located in HIF3A, EBF4, and an intergenic region nearest to GLI2 (distance 57,533 bp). Five CpG-sites, all in proximity to GLI2, were hypermethylated in VLBW and associated with lower birth weight in the meta-analysis.
Conclusion: We identified differentially methylated CpG-sites suggesting an epigenetic signature of preterm birth at VLBW present in adult life.
Impact: Being born preterm at very low birth weight has major implications for later health and chronic disease risk factors. The mechanism linking preterm birth to later outcomes remains unknown. Our cohort study of 157 very low birth weight adults and 161 controls found 66 differentially methylated sites at mean age of 22 years. Our findings suggest an epigenetic mark of preterm birth present in adulthood, which opens up opportunities for mechanistic studies.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study protocol was approved by the Northern Ostrobothnia Hospital District Ethical Committee (94/2011 (12.12.2011) for NFBC1966 and 108/2017 (15.1.2018) for NFBC1986), the Ethics Committee of Children’s and Adolescent’s Diseases and Psychiatry at Helsinki and Uusimaa Hospital District (HeSVA and PREDO), and the City of Helsinki and Helsinki and Uusimaa Hospital District (GLAKU). Written informed consent was given by all adult participants and parent/guardian by the minors. No individual-level data is presented anywhere in the manuscript.
Figures


Similar articles
-
DNA methylation patterns at birth predict health outcomes in young adults born very low birthweight.Clin Epigenetics. 2023 Mar 23;15(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s13148-023-01463-3. Clin Epigenetics. 2023. PMID: 36959629 Free PMC article.
-
Altered Methylation of IGF2 Locus 20 Years after Preterm Birth at Very Low Birth Weight.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 19;8(6):e67379. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067379. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23840686 Free PMC article.
-
Body composition in adults born preterm with very low birth weight.Pediatr Res. 2024 Apr;95(5):1316-1324. doi: 10.1038/s41390-023-02896-5. Epub 2023 Nov 16. Pediatr Res. 2024. PMID: 37973945 Free PMC article.
-
Blood Pressure in Young Adults Born at Very Low Birth Weight: Adults Born Preterm International Collaboration.Hypertension. 2016 Oct;68(4):880-7. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.116.08167. Epub 2016 Aug 29. Hypertension. 2016. PMID: 27572149 Review.
-
Multidisciplinary and neuroimaging findings in preterm born very low birthweight individuals from birth to 28 years of age: A systematic review of a Norwegian prospective cohort study.Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2022 Sep;36(5):606-630. doi: 10.1111/ppe.12890. Epub 2022 Jul 22. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2022. PMID: 35867340 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hovi, P. et al. Glucose regulation in young adults with very low birth weight. N. Engl. J. Med.356, 2053–2063 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Hovi, P. et al. Blood pressure in young adults born at very low birth weight: adults born preterm international collaboration. Hypertension68, 880–887 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Saarenpaa, H. K. et al. Lung function in very low birth weight adults. Pediatrics136, 642–650 (2015). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

