Work-related support for employed and self-employed people with rheumatoid arthritis or axial spondyloarthritis: a cross-sectional online survey of patients
- PMID: 38898306
- PMCID: PMC11222234
- DOI: 10.1007/s00296-024-05643-z
Work-related support for employed and self-employed people with rheumatoid arthritis or axial spondyloarthritis: a cross-sectional online survey of patients
Abstract
Background: Little is known about the provision of work-related support for (self-)employed people with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) by healthcare providers (HCPs) or employers.
Objective: This study aims to explore the experiences of (self-)employed people with RA or axSpA regarding work-related support from HCPs and employers in the Netherlands.
Methods: This cross-sectional study concerned an online survey for (self-)employed people, aged ≥ 16 years and diagnosed with RA or axSpA. The survey focused on experiences with HCPs and employers' work-related support and included questions on sociodemographic factors, health and work characteristics and work-related problems.
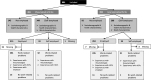
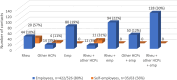
Results: The survey was completed by 884 participants, 56% with RA and 44% with axSpA, of whom 65% were employed, 8% self-employed and 27% not employed. In total, 95% (589/617) of (self-)employed participants reported work-related problems. Sixty-five percent of employed and 56% of self-employed participants had discussed these work-related problems with rheumatologists and/or other HCPs. Whereas 69% of employees with their employer. Both employed and self-employed participants reported that work-related advices or actions were more often provided by other HCPs (53%) than rheumatologists (29%). Fifty-six percent of employees reported this work-related support by the employer.
Conclusion: This survey among (self-)employed people with RA or axSpA found that the majority reported work-related problems, but only half of them received any work-related support for these problems. Discussion of work-related problems with HCPs was more often reported by employed than self-employed participants. More attention from especially rheumatologists and other HCPs is important to identify and address work-related problems promptly.
Keywords: Axial spondyloarthritis; Cross-sectional study; Rheumatoid arthritis; Surveys and questionnaires; Vocational rehabilitation; Work.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
N.F. Bakker, S.F.E. van Weely, T.P.M. Vliet Vlieland and J. Knoop declare that they have no conflict of interest. A. Boonen received research grants from Abbvie and Lilly, and honoraria for lectures or consultation from Pfizer, Novartis, UCB, Abbvie and Galapagos; all to her department.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development and application of a questionnaire to assess patient beliefs in rheumatoid arthritis and axial spondyloarthritis.Clin Rheumatol. 2018 Oct;37(10):2649-2657. doi: 10.1007/s10067-018-4172-5. Epub 2018 Jun 12. Clin Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 29948351 Free PMC article.
-
Sociodemographic and clinical variables associated with negative illness perception in patients newly diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis, axial spondyloarthritis, or psoriatic arthritis-a survey based cross-sectional study.Rheumatol Int. 2024 Jun;44(6):1119-1131. doi: 10.1007/s00296-024-05553-0. Epub 2024 Apr 2. Rheumatol Int. 2024. PMID: 38563971 Free PMC article.
-
A mixed methods study to uncover impediments to accurate diagnosis of nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis in the USA.Clin Rheumatol. 2023 Oct;42(10):2811-2822. doi: 10.1007/s10067-023-06671-z. Epub 2023 Jun 22. Clin Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 37347434
-
Work limitations and associated factors in rheumatoid arthritis, axial spondyloarthritis, osteoarthritis and fibromyalgia.Musculoskeletal Care. 2023 Sep;21(3):827-844. doi: 10.1002/msc.1760. Epub 2023 Mar 28. Musculoskeletal Care. 2023. PMID: 36975543 Review.
-
Quality of reporting and nature of harms in clinical trials on supervised exercise in patients with rheumatoid arthritis or axial spondyloarthritis.Rheumatol Int. 2024 Jan;44(1):25-39. doi: 10.1007/s00296-023-05502-3. Epub 2023 Nov 30. Rheumatol Int. 2024. PMID: 38030947
Cited by
-
Trends in work participation among patients with inflammatory rheumatic musculoskeletal diseases (iRMDs): Data from the German National Database (2010-2022).RMD Open. 2025 Jan 25;11(1):e004980. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2024-004980. RMD Open. 2025. PMID: 39863303 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mielants H, Van den Bosch F. Extra-articular manifestations. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2009;27(4 Suppl 55):S56–61. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical