A Systematic Review to Summarise and Appraise the Reporting of Surgical Innovation: a Case Study in Robotic Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass
- PMID: 38898310
- PMCID: PMC11289006
- DOI: 10.1007/s11695-024-07329-8
A Systematic Review to Summarise and Appraise the Reporting of Surgical Innovation: a Case Study in Robotic Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass
Abstract
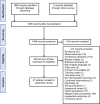
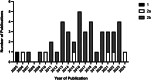
Robotic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RRYGB) is an innovative alternative to traditional laparoscopic approaches. Literature has been published investigating its safety/efficacy; however, the quality of reporting is uncertain. This systematic review used the Idea, Development, Exploration, Assessment and Long-term follow-up (IDEAL) framework to assess the reporting quality of available literature. A narrative summary was formulated, assessing how comprehensively governance/ethics, patient selection, demographics, surgeon expertise/training, technique description and outcomes were reported. Forty-seven studies published between 2005 and 2024 were included. There was incomplete/inconsistent reporting of governance/ethics, patient selection, surgeon expertise/training and technique description, with heterogenous outcome reporting. RRYGB reporting was poor and did not align with IDEAL guidance. Robust prospective studies reporting findings using IDEAL/other guidance are required to facilitate safe widespread adoption of RRYGB and other surgical innovations.
Keywords: Bariatric surgery; IDEAL framework; Innovation; Outcome reporting; Robotic surgery; Roux-en-Y gastric bypass.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
This study is supported by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Biomedical Research Centre (BRC) at the University Hospitals Bristol and Weston NHS Foundation Trust and the University of Bristol. The views expressed are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the UK National Health Service, National Institute for Health Research, or Department of Health. NB is a Medical Research Council Clinician Scientist. No authors declare any conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Tian HL, Tian JH, Yang KH, et al. The effects of laparoscopic vs. open gastric bypass for morbid obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obes Rev. 2011;12:254–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

