Production of grains with ultra-low heavy metal accumulation by pyramiding novel Alleles of OsNramp5 and OsLsi2 in two-line hybrid rice
- PMID: 38898780
- PMCID: PMC11536454
- DOI: 10.1111/pbi.14414
Production of grains with ultra-low heavy metal accumulation by pyramiding novel Alleles of OsNramp5 and OsLsi2 in two-line hybrid rice
Abstract
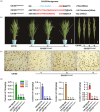
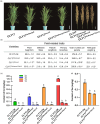
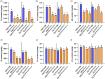
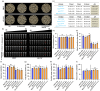
Ensuring rice yield and grain safety quality are vital for human health. In this study, we developed two-line hybrid rice (TLHR) with ultra-low grain cadmium (Cd) and arsenic (As) accumulation by pyramiding novel alleles of OsNramp5 and OsLsi2. We first generated low Cd accumulation restorer (R) lines by editing OsNramp5, OsLCD, and OsLCT1 in japonica and indica. After confirming that OsNramp5 was most efficient in reducing Cd, we edited this gene in C815S, a genic male sterile line (GMSL), and screened it for alleles with low Cd accumulation. Next, we generated R and GMSL lines with low As accumulation by editing OsLsi2 in a series of YK17 and C815S lines. When cultivated in soils that were heavily polluted with Cd and As, the edited R, GMSL, and TLHR plants showed significantly reduced heavy metal accumulation, while maintaining a relatively stable yield potential. This study provides an effective scheme for the safe production of grains in As- and/or Cd-polluted paddy fields.
Keywords: Ultra‐low heavy metal accumulation; arsenic; cadmium; gene pyramiding; grain safety; two‐line hybrid rice.
© 2024 The Author(s). Plant Biotechnology Journal published by Society for Experimental Biology and The Association of Applied Biologists and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
OsHMA3 overexpression works more efficiently in generating low-Cd rice grain than OsNramp5 knockout mutation.BMC Res Notes. 2025 Feb 5;18(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s13104-025-07112-7. BMC Res Notes. 2025. PMID: 39910580 Free PMC article.
-
A weak allele of OsNRAMP5 confers moderate cadmium uptake while avoiding manganese deficiency in rice.J Exp Bot. 2022 Oct 18;73(18):6475-6489. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erac302. J Exp Bot. 2022. PMID: 35788288
-
Knockout of OsNramp5 using the CRISPR/Cas9 system produces low Cd-accumulating indica rice without compromising yield.Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 31;7(1):14438. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-14832-9. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29089547 Free PMC article.
-
Route and Regulation of Zinc, Cadmium, and Iron Transport in Rice Plants (Oryza sativa L.) during Vegetative Growth and Grain Filling: Metal Transporters, Metal Speciation, Grain Cd Reduction and Zn and Fe Biofortification.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Aug 13;16(8):19111-29. doi: 10.3390/ijms160819111. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26287170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of Reducing Cadmium Pollution in the Rice-Soil System in China.Foods. 2025 May 14;14(10):1747. doi: 10.3390/foods14101747. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40428525 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of Cd and As accumulation and subcellular distribution in different varieties of perennial ryegrasses.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Apr 22;25(1):508. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06530-w. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40259279 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Transcriptome Analysis Within the Realm of Low Arsenic Rice Breeding.Plants (Basel). 2025 Feb 17;14(4):606. doi: 10.3390/plants14040606. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40006866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
OsHMA3 overexpression works more efficiently in generating low-Cd rice grain than OsNramp5 knockout mutation.BMC Res Notes. 2025 Feb 5;18(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s13104-025-07112-7. BMC Res Notes. 2025. PMID: 39910580 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Das, S. , Chou, M.L. , Jean, J.S. , Liu, C.C. and Yang, H.J. (2016) Water management impacts on arsenic behavior and rhizosphere bacterial communities and activities in a rice agro‐ecosystem. Sci. Total Environ. 542, 642–652. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

