Lysine-Rich Polypeptide Modulates Forkhead Box O3 and Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase-Protein Kinase B Pathway To Induce Apoptosis in Breast Cancer
- PMID: 38898949
- PMCID: PMC11184599
- DOI: 10.1021/acsptsci.4c00221
Lysine-Rich Polypeptide Modulates Forkhead Box O3 and Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase-Protein Kinase B Pathway To Induce Apoptosis in Breast Cancer
Abstract
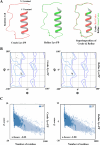
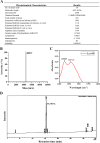
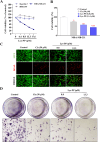
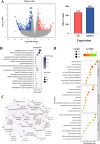
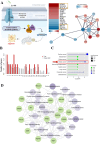
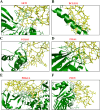
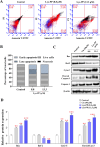
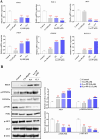
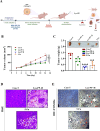
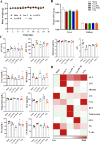
The PI3K/AKT/FOXO3 pathway is one of the most frequently involved signaling pathways in cancer, including breast cancer. Therefore, we synthesized a novel lysine-rich polypeptide (Lys-PP) using de novo assembly method and evaluated its anticancer effect. We characterized the structural and physicochemical properties of Lys-PP using various techniques. Later, we used integrated approaches such as in silico, in vitro, and in vivo analysis to confirm the anticancer and therapeutic effect of Lys-PP. First, RNA sequencing suggests Lys-PP disrupted the central carbon metabolic pathway through the modulation of prolactin signaling. Additionally, docking analysis also confirmed the significant association of PI3K/AKT and FOXO3 pathway to induce an apoptotic effect on cancer. Second, Lys-PP exhibited a significant cytotoxicity effect against MDA-MB-231 but no cytotoxic effects on RAW 264.7 and HEK-293, respectively. The cytotoxic effect of Lys-PP-induced apoptosis by an increase in FOXO3a protein expression and a decrease in PI3K/AKT pathway was confirmed by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction, immunoblotting, and fluorescent microscopy. Later, immunohistochemistry and hematoxylin and eosin staining on MDA-MD-231 showed increased FOXO3a expression and cell death in the xenograft mice model. Further, liver function, metabolic health, or lipid profile upon Lys-PP showed the absence of significant modulation in the biomarkers except for kidney-related biomarkers. Overall, our comprehensive study provides the first evidence of Lys-PP antibreast cancer action, which could serve as a potential treatment in an alternative or complementary medicine practice.
© 2024 American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abo-El-Rejal A.; Ayman S.; Aymen F. Advances in breast cancer segmentation: A comprehensive review. Acadlore Transactions on AI and Machine Learning 2024, 3 (2), 70–83. 10.56578/ataiml030201. - DOI
-
- Elbasyouni A.; Soro O.; Nshimirimana J. J. I. J. O. R. Understanding Breast Cancer: A Key Emphasis on Molecular Signalling Pathways and Phytotherapy. Int. J. Oncol. Radiother. 2023, 4 (2), 1–5. 10.51626/ijor.2023.04.00028. - DOI
-
- Alkhatabi H. A.; Zohny S. F.; Shait Mohammed M. R.; Choudhry H.; Rehan M.; Ahmad A.; Ahmed F.; Khan M. I.. Venetoclax-Resistant MV4–11 Leukemic Cells Activate PI3K/AKT Pathway for Metabolic Reprogramming and Redox Adaptation for Survival. Antioxidants 2022, 11 ( (3), ). DOI: 461.10.3390/antiox11030461. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Soltani A.; Torki S.; Ghahfarokhi M. S.; Jami M. S.; Ghatrehsamani M. Targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT pathways by small molecules and natural compounds as a therapeutic approach for breast cancer cells. Molecular biology reports 2019, 46 (5), 4809–4816. 10.1007/s11033-019-04929-x. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
