Neurophobia and its Correlates among Undergraduate Clinical Students in a Nigerian Private University
- PMID: 38898964
- PMCID: PMC11185803
Neurophobia and its Correlates among Undergraduate Clinical Students in a Nigerian Private University
Abstract
Background: The fear of neurology and neurosciences has been referred to as neurophobia. Neurophobia is a global phenomenon, that is worse in sub-Saharan Africa due to its impact on the already established huge gap in the neurologist-to-population ratio. The need to identify modifiable factors that could curb neurophobia stirred the current study, which aimed to determine the correlates of neurophobia among undergraduate clinical students.
Methodology: A cross-sectional design was adopted involving 173 undergraduate clinical students selected via stratified sampling. Content validated, self-administered questionnaire was utilized to obtain data on the perception of neurology, neurophobia, and demographic/academic-related characteristics. Bivariate and multivariate analyses were performed at the 0.05 significant level.
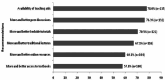
Results: The mean age (±SD) of the participants was 25.8(±2.2) years with a male-to-female ratio of 1:1.2. More than half of the undergraduate clinical students perceived neurology as being badly taught (77.5%), difficult to learn (83.2%), and with complex clinical examination (85.5%). The prevalence of neurophobia was 76.3% (n=132). The significant correlate of neurophobia was perceived poor knowledge of neurology. Students with poor perceived knowledge of neurology were about two times more likely to have neurophobia than those with perceived good knowledge (AOR=2.14; 95%CI: 1.04-4.41).
Conclusion: Approximately 8 in 10 undergraduate clinical students in Nigeria have neurophobia and the significant determining factor is their perceived poor knowledge. The need to adopt educational models that would strengthen academic prowess in neurology is strongly advocated as most of the students felt that the course was being badly taught.
Key messages: Neurophobia among clinical undergraduate students is rampant, and without timely educational intervention, the existing wide gap in the neurologist-to-population ratio could worsen. Our findings highlight the dire need to institute educational models tailored to attaining better teaching aids, peer discussions, and bedside teaching among clinical undergraduate students.
Keywords: Clinical Students; Medical Education; Neurology; Neurophobia.
Copyright © 2023 Nigerian Medical Association.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neurophobia among undergraduate medical students: a European experience beyond the Anglosphere.Rev Neurol. 2023 Jun 1;76(11):351-359. doi: 10.33588/rn.7611.2023102. Rev Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37231548 Free PMC article. English, Spanish.
-
Perception of neurology among undergraduate medical students - what can be done to counter neurophobia during clinical studies?BMC Med Educ. 2023 Jun 16;23(1):447. doi: 10.1186/s12909-023-04405-y. BMC Med Educ. 2023. PMID: 37328733 Free PMC article.
-
Neurophobia in medical students and junior doctors--blame the GIK.Ann Acad Med Singap. 2013 Nov;42(11):559-66. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2013. PMID: 24356651
-
Preventing "Neurophobia": Remodeling Neurology Education for 21st-Century Medical Students through Effective Pedagogical Strategies for "Neurophilia".Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2018 Jan-Mar;21(1):9-18. doi: 10.4103/aian.AIAN_371_17. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29720792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurophobia amongst medical students: Hype or reality.Brain Spine. 2024 Nov 12;4:104134. doi: 10.1016/j.bas.2024.104134. eCollection 2024. Brain Spine. 2024. PMID: 39687082 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Level of knowledge and perceived challenges associated with learning movement disorders topics: a critical review of final-year medical students at a Nigerian private university.Niger Med J. 2024 Jun 20;65(3):292-300. doi: 10.60787/nmj-v65i3-371. eCollection 2024 May-Jun. Niger Med J. 2024. PMID: 39022571 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jozefowicz RF. Neurophobia: the fear of neurology among medical students. Arch Neurol. 1994; 51:328–9. - PubMed
-
- Silberberg D, Katabira E. Neurological Disorders. Disease Mortality Sub-Saharan Africa. International Bank Reconstruction and Development World Bank, 2006. p.2295. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK2295/ [cited 2022 Jul 4];
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). Neurological Disorders: Public Health Challenges. Geneva, Switzerland. 2006. p. 1–209. Available from: https://books.google.com.ng/books?hl=en&lr=&id=Z8uwPwlPUw4C&oi=fnd&pg=PR... DISORDERS public health challenges&f=false [cited 2022 Jul 4].
-
- European Federation of Neurological Societies. The Education Committee of EFNS: activities and work in progress. Eur J Neurol. 2003; 10:205–211. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous