A Comparative Analysis of Laboratory Parameters of Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients by Disease Severity and Mortality at a Facility in Ibadan, Nigeria
- PMID: 38898975
- PMCID: PMC11185805
A Comparative Analysis of Laboratory Parameters of Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients by Disease Severity and Mortality at a Facility in Ibadan, Nigeria
Abstract
Background: COVID-19, which is caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, is associated with abnormalities of biochemical parameters. There are indications that some of these biochemical parameters can differ according to the severity of the disease and the outcome of the infection. This study describes and compares laboratory findings among COVID-19 patients hospitalized at a facility in Southwestern Nigeria according to disease severity and mortality.
Methodology: Records of 223 patients with COVID-19 disease admitted between March 2020 and May 2021 were retrospectively collected. Socio-demographic characteristics, laboratory parameters, and patient outcomes were obtained. Patients were classified according to COVID-19 severity. Laboratory parameters were compared between patients with severe and non-severe disease and between survivors and non-survivors.
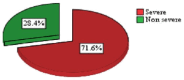
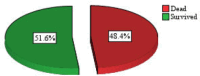
Results: Of the 215 patients with some laboratory data included in the analysis, there were 133 (62%) males, and 56.7% were aged above 60 years. A total of 71.6% had severe COVID-19 and 48.4% died during hospitalization. The severe disease occurred significantly more frequently among non-survivors (P0.01). Higher leukocyte and neutrophil counts, urea levels, D-Dimer, and fasting blood glucose levels occurred significantly more frequently in both severe disease and mortality categories. Additionally, elevated GGT and CRP were significantly more common in those with severe than non-severe disease while lower hemoglobin, hematocrit, albumin, and higher creatinine levels were significantly more common in non-survivors.
Conclusion: Our study found that certain readily obtainable biochemical parameters occur more frequently with severe disease and/or mortality amongst patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in sub-Saharan Africa and might be useful for prognostication and allocation of resources.
Keywords: Biochemical Markers; COVID-19; Hematological Indices; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2023 Nigerian Medical Association.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Poor Prognostic Biochemical Markers Predicting Fatalities Caused by COVID-19: A Retrospective Observational Study From a Developing Country.Cureus. 2020 Aug 5;12(8):e9575. doi: 10.7759/cureus.9575. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 32913691 Free PMC article.
-
Hematological and Biochemical Laboratory Parameters in COVID-19 Patients: A Retrospective Modeling Study of Severity and Mortality Predictors.Biomed Res Int. 2023 Nov 18;2023:7753631. doi: 10.1155/2023/7753631. eCollection 2023. Biomed Res Int. 2023. PMID: 38027038 Free PMC article.
-
Using laboratory parameters as predictors for the severity and mortality of COVID-19 in hospitalized patients.Pharm Pract (Granada). 2022 Jul-Sep;20(3):2721. doi: 10.18549/PharmPract.2022.3.2721. Epub 2022 Sep 9. Pharm Pract (Granada). 2022. PMID: 36733508 Free PMC article.
-
Hematologic, biochemical and immune biomarker abnormalities associated with severe illness and mortality in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a meta-analysis.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2020 Jun 25;58(7):1021-1028. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2020-0369. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2020. PMID: 32286245 Review.
-
Laboratory features of severe vs. non-severe COVID-19 patients in Asian populations: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Med Res. 2020 Aug 3;25(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s40001-020-00432-3. Eur J Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32746929 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wolde M. Hematology, immunology and clinical chemistry profiles of COVID-19 patients: Systematic review. Ethiop J Heal Dev. 2020; 34:226–31.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous