Bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study of association between smoking initiation and atrial fibrillation
- PMID: 38899119
- PMCID: PMC11186308
- DOI: 10.18332/tid/189380
Bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study of association between smoking initiation and atrial fibrillation
Abstract
Introduction: The relationship between smoking and heart disease has been frequently reported. Therefore, we aimed to explore the association between smoking initiation and atrial fibrillation.
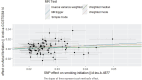
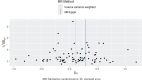
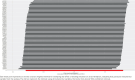
Methods: Genetic association data pertaining to smoking initiation and atrial fibrillation were obtained from genome-wide association studies (GWAS). Phenotypically related single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were selected as instrumental variables. Inverse-variance weighted (IVW), weighted median, Mendelian randomization (MR), Egger regression, simple mode, and weighted mode methods were employed to perform the MR study. The association between smoking initiation and atrial fibrillation was evaluated using odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI). Cochran's Q test was employed to assess heterogeneity among instrumental variables, utilizing the IVW and MR-Egger methods. The Egger-intercept method was employed to test for horizontal pleiotropy, and the 'leave-one-out' method was utilized for sensitivity analysis.
Results: The MR results for the effect of smoking initiation on atrial fibrillation (IVW, OR=1.11; 95% CI: 1.02-1.20, p=0.013) supported an association between smoking initiation and an increased likelihood of atrial fibrillation. In total, 85 SNPs were extracted from the GWAS pooled data as instrumental variables. The MR-Egger method indicated an intercept close to 0 (Egger intercept= -0.005, p=0.371), suggesting no horizontal pleiotropy in the selected instrumental variables. The 'leave-one-out' sensitivity analysis demonstrated that the results were robust and that no instrumental variables significantly influenced the results. Reverse MR analysis indicated no effect of atrial fibrillation on smoking initiation (IVW, OR=1.00; 95% CI: 0.99-1.02, p=0.684).
Conclusions: Smoking initiation has a significant impact on atrial fibrillation. However, atrial fibrillation did not influence smoking initiation. This study provides novel insights into the genetic relationships between smoking initiation and atrial fibrillation.
Keywords: atrial fibrillation; smoking initiation; two-sample Mendelian randomization.
© 2024 Wu Z. et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have completed and submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest and none was reported.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Genetic Causation Analysis of Hyperandrogenemia Testing Indicators and Preeclampsia].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 May 20;55(3):566-573. doi: 10.12182/20240560106. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 38948277 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Type 1 diabetes mellitus increases the risk of sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 Nov 28;49(11):1821-1827. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2024.240375. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 40177765 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Genetic causal relationship between age at menarche and benign oesophageal neoplasia identified by a Mendelian randomization study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 21;14:1113765. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1113765. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37025412 Free PMC article.
-
Causal relationship between type I diabetes mellitus and atrial fibrillation: A Mendelian randomization study.Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2025 Mar 11;57:101643. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2025.101643. eCollection 2025 Apr. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2025. PMID: 40129655 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic insights into the causal relationship between air pollutants and atrial fibrillation: a Mendelian randomization study.Int J Environ Health Res. 2025 May 16:1-11. doi: 10.1080/09603123.2025.2502635. Online ahead of print. Int J Environ Health Res. 2025. PMID: 40376711 Review.
Cited by
-
Incorporating the STOP-BANG questionnaire improves prediction of cardiovascular events during hospitalization after myocardial infarction.Sci Rep. 2025 May 31;15(1):19180. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-03882-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40450044 Free PMC article.
-
Novel predictive role of glomerular filtration rate in atrial fibrillation development among chronic heart failure patients.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025 Jul 10;25(1):503. doi: 10.1186/s12872-025-04966-4. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025. PMID: 40640715 Free PMC article.
-
Unmasking Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with COPD at Primary Care Settings: The Critical Role of Age, Sex, and Smoking.J Clin Med. 2025 Feb 21;14(5):1444. doi: 10.3390/jcm14051444. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40094882 Free PMC article.
-
The genomic bases of atrial fibrillation in an Ecuadorian patient: a case report.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Jun 23;12:1552417. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1552417. eCollection 2025. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40625395 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
