Inhibition of Interleukin-33 to Reduce Glomerular Endothelial Inflammation in Diabetic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 38899206
- PMCID: PMC11184260
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ekir.2024.03.009
Inhibition of Interleukin-33 to Reduce Glomerular Endothelial Inflammation in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Abstract
Introduction: Inflammation is a significant contributor to cardiorenal morbidity and mortality in diabetic kidney disease (DKD). The pathophysiological mechanisms linking systemic, subacute inflammation and local, kidney injury-initiated immune maladaptation is partially understood.
Methods: Here, we explored the expression of proinflammatory cytokines in patients with DKD; investigated mouse models of type 1 and type 2 diabetes (T2D); evaluated glomerular signaling in vitro; performed post hoc analyses of systemic and urinary markers of inflammation; and initiated a phase 2b clinical study (FRONTIER-1; NCT04170543).
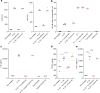
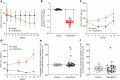
Results: Transcriptomic profiling of kidney biopsies from patients with DKD revealed significant glomerular upregulation of interleukin-33 (IL-33). Inhibition of IL-33 signaling reduced glomerular damage and albuminuria in the uninephrectomized db/db mouse model (T2D/DKD). On a cellular level, inhibiting IL-33 improved glomerular endothelial health by decreasing cellular inflammation and reducing release of proinflammatory cytokines. Therefore, FRONTIER-1 was designed to test the safety and efficacy of the IL-33-targeted monoclonal antibody tozorakimab in patients with DKD. So far, 578 patients are enrolled in FRONTIER-1. The baseline inflammation status of participants (N > 146) was assessed in blood and urine. Comparison to independent reference cohorts (N > 200) validated the distribution of urinary tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 (TNFR1) and C-C motif chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2). Treatment with dapagliflozin for 6 weeks did not alter these biomarkers significantly.
Conclusion: We show that blocking the IL-33 pathway may mitigate glomerular endothelial inflammation in DKD. The findings from the FRONTIER-1 study will provide valuable insights into the therapeutic potential of IL-33 inhibition in DKD.
Keywords: IL-33; biomarker; diabetic kidney disease; inflammation; phase 2b; tozorakimab.
© 2024 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures





References
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

