The amygdaloid body of the family Delphinidae: a morphological study of its central nucleus through calbindin-D28k
- PMID: 38899230
- PMCID: PMC11186458
- DOI: 10.3389/fnana.2024.1382036
The amygdaloid body of the family Delphinidae: a morphological study of its central nucleus through calbindin-D28k
Abstract
Introduction: The amygdala is a noticeable bilateral structure in the medial temporal lobe and it is composed of at least 13 different nuclei and cortical areas, subdivided into the deep nuclei, the superficial nuclei, and the remaining nuclei which contain the central nucleus (CeA). CeA mediates the behavioral and physiological responses associated with fear and anxiety through pituitary-adrenal responses by modulating the liberation of the hypothalamic Corticotropin Releasing Factor/Hormone.
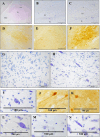
Methods: Five dolphins of three different species, belonging to the family Delphinidae (three striped dolphins, one common dolphin, and one Atlantic spotted dolphin), were used for this study. For a precise overview of the CeA's structure, thionine staining and the immunoperoxidase method using calbindin D-28k were employed.
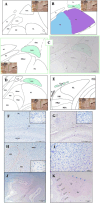
Results: CeA extended mainly dorsal to the lateral nucleus and ventral to the striatum. It was medial to the internal capsule and lateral to the optic tract and the medial nucleus of the amygdala.
Discussion: The dolphin amygdaloid complex resembles that of primates, including the subdivision, volume, and location of the CeA.
Keywords: amygdaloid body; calbindin-D28k; central nucleus of the amygdala; dolphins; toothed whales.
Copyright © 2024 Sacchini, Bombardi, Arbelo and Herráez.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Distribution of calbindin-D28k immunoreactivity in the monkey temporal lobe: the amygdaloid complex.J Comp Neurol. 1993 May 8;331(2):199-224. doi: 10.1002/cne.903310205. J Comp Neurol. 1993. PMID: 7685361
-
Calbindin-D28K-immunoreactive cells and fibres in the human amygdaloid complex.Neuroscience. 1996 Nov;75(2):421-43. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(96)00296-5. Neuroscience. 1996. PMID: 8931007
-
Coexistence of peptides (corticotropin releasing factor/neurotensin and substance P/somatostatin) in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis and central amygdaloid nucleus of the rat.Neuroscience. 1989;30(2):377-83. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90259-5. Neuroscience. 1989. PMID: 2473417
-
CRH: the link between hormonal-, metabolic- and behavioral responses to stress.J Chem Neuroanat. 2013 Dec;54:25-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jchemneu.2013.05.003. Epub 2013 Jun 15. J Chem Neuroanat. 2013. PMID: 23774011 Review.
-
Role of the extended amygdala in short-duration versus sustained fear: a tribute to Dr. Lennart Heimer.Brain Struct Funct. 2008 Sep;213(1-2):29-42. doi: 10.1007/s00429-008-0183-3. Epub 2008 Jun 5. Brain Struct Funct. 2008. PMID: 18528706 Review.
References
-
- Bombardi C., Grandis A., Chiocchetti R., Lucchi M. L. (2006). Distribution of calbindin-D28k, neuronal nitric oxide synthase, and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate diaphorase (NADPH-d) in the lateral nucleus of the sheep amygdaloid complex. Anat. Embryol. 211 707–720. 10.1007/s00429-006-0133-x - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

