Decreased Ocular Perfusion Pressure Associated With Reverse Ophthalmic Artery Flow on Transcranial Doppler Ultrasonography
- PMID: 38899251
- PMCID: PMC11186674
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.60706
Decreased Ocular Perfusion Pressure Associated With Reverse Ophthalmic Artery Flow on Transcranial Doppler Ultrasonography
Abstract
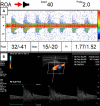
Innovative applications of clinical ocular diagnostic tools are emerging to help identify systemic disorders that extend beyond ocular diseases. Ophthalmodynamometry (ODM) is a screening tool that non-invasively determines mean central retinal artery pressure (MCRAP) and ocular perfusion pressure (OPP). Decreased OPP and MCRAP on Falck Medical Multifunctional Device (FMD, Falck Medical, Inc., Mystic, CT), along with reverse ophthalmic artery flow (ROAF) on transcranial Doppler ultrasonography (TCD), indicate increased collateral brain perfusion and possible stenosis of the ophthalmic artery or internal carotid artery (ICA). In this case report, we describe the case of a 78-year-old female with ROAF, reduced MCRAP, and OPP in the right eye, confirmed by carotid duplex of 50-79% right ICA stenosis. Early application of ODM and TCD allowed for prompt diagnosis and management with a vascular specialist.
Keywords: cerebrovascular occlusive disease; mean central retinal artery pressure; ocular perfusion pressure; ophthalmodynamometry; reverse ophthalmic artery flow; transcranial doppler ultrasonography.
Copyright © 2024, Murillo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Color Doppler imaging of orbital arteries for detection of carotid occlusive disease.Stroke. 1993 Aug;24(8):1196-203. doi: 10.1161/01.str.24.8.1196. Stroke. 1993. PMID: 8342197
-
Collateral blood supply through the ophthalmic artery: a steal phenomenon analyzed by color Doppler imaging.Ophthalmology. 1998 Apr;105(4):689-93. doi: 10.1016/S0161-6420(98)94025-8. Ophthalmology. 1998. PMID: 9580236
-
Transcranial Doppler ultrasonography in neurological surgery and neurocritical care.Neurosurg Focus. 2019 Dec 1;47(6):E2. doi: 10.3171/2019.9.FOCUS19611. Neurosurg Focus. 2019. PMID: 31786564 Review.
-
Non-invasive Assessment of Central Retinal Artery Pressure: Age and Posture-dependent Changes.Curr Eye Res. 2021 Jan;46(1):135-139. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2020.1772833. Epub 2020 Jun 4. Curr Eye Res. 2021. PMID: 32441142 Free PMC article.
-
Blindness Following Carotid Artery Stenting Due to Ocular Hyperperfusion - Report and Review of Literature.Neurol India. 2020 Jul-Aug;68(4):897-899. doi: 10.4103/0028-3886.293455. Neurol India. 2020. PMID: 32859837 Review.
References
-
- Ophthalmic artery flow direction on color flow duplex imaging is highly specific for severe carotid stenosis. Reynolds PS, Greenberg JP, Lien LM, Meads DC, Myers LG, Tegeler CH. J Neuroimaging. 2002;12:5–8. - PubMed
-
- Reversal of ophthalmic artery flow as a predictor of intracranial hemodynamic compromise: implication for prognosis of severe carotid stenosis. Tsai CL, Lee JT, Cheng CA, Liu MT, Chen CY, Hu HH, Peng GS. Eur J Neurol. 2013;20:564–570. - PubMed
-
- Ophthalmodynamometry in internal carotid artery occlusion. Paulson OB. Stroke. 1976;7:564–566. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
