Conversion therapy of a giant hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein thrombus and inferior vena cava thrombus: A case report and review of literature
- PMID: 38899296
- PMCID: PMC11185326
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i16.2847
Conversion therapy of a giant hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein thrombus and inferior vena cava thrombus: A case report and review of literature
Abstract
Background: The prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) combined with portal and hepatic vein cancerous thrombosis is poor, for unresectable patients the combination of targeted therapy and immune therapy was the first-line recommended treatment for advanced HCC, with a median survival time of only about 2.7-6 months. In this case report, we present the case of a patient with portal and hepatic vein cancerous thrombosis who achieved pathologic complete response after conversion therapy.
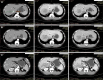
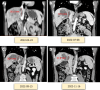
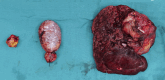
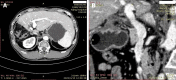
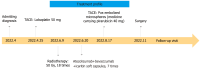
Case summary: In our center, a patient with giant HCC combined with portal vein tumor thrombus and hepatic vein tumor thrombus was treated with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE), radiotherapy, targeted therapy and immunotherapy, and was continuously given icaritin soft capsules for oral regulation. After 7 months of conversion therapy, the patient's tumor shrank and the tumor thrombus subsided significantly. The pathology of surgical resection was in complete remission, and there was no progression in the postoperative follow-up for 7 months, which provided a basis for the future strategy of combined conversion therapy.
Conclusion: In this case, atezolizumab, bevacizumab, icaritin soft capsules combined with radiotherapy and TACE had a good effect. For patients with hepatocellular carcinoma combined with hepatic vein/inferior vena cava tumor thrombus, adopting a high-intensity, multimodal proactive strategy under the guidance of multidisciplinary team (MDT) is an important attempt to break through the current treatment dilemma.
Keywords: Case report; Conversion; Downstaging; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Icaritin; Portal vein thrombus.
©The Author(s) 2024. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Robot Assisted Laparoscopy Combined with Thoracoscopy in the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Inferior Vena Cava Tumor Thrombus.Ann Surg Oncol. 2023 Sep;30(9):5447-5449. doi: 10.1245/s10434-023-13512-5. Epub 2023 Jun 7. Ann Surg Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37285097
-
Conversion surgery for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus after successful atezolizumab plus bevacizumab therapy: a case report.World J Surg Oncol. 2022 Jul 12;20(1):228. doi: 10.1186/s12957-022-02691-2. World J Surg Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35831894 Free PMC article.
-
Aggressive Multidisciplinary Treatment for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Achievement of a Pathologic Complete Response and Long-Term Survival.Ann Surg Oncol. 2025 Mar;32(3):1819-1820. doi: 10.1245/s10434-024-16622-w. Epub 2024 Dec 13. Ann Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39671164
-
Favorable response to multimodal treatment in hepatocellular carcinoma with inferior vena cava and right atrial tumor thrombus and left adrenal gland metastasis: A case report and literature review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Dec 10;100(49):e27987. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000027987. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 34889243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The treatment of transarterial chemoembolization/hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy combined with lenvatinib and PD-1 inhibitor is effective against hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: A systematic review.Front Oncol. 2023 Mar 9;13:1054072. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1054072. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36969065 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Conversion therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma to improve treatment strategies for intermediate and advanced stages.World J Clin Cases. 2024 Oct 6;12(28):6241-6243. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i28.6241. World J Clin Cases. 2024. PMID: 39371556 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pawarode A, Voravud N, Sriuranpong V, Kullavanijaya P, Patt YZ. Natural history of untreated primary hepatocellular carcinoma: A retrospective study of 157 patients. Am J Clin Oncol. 1998;21:386–391. - PubMed
-
- Chinese Society of Liver Cancer Chinese Medical Doctor Association. [Chinese expert consensus on multidisciplinary diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus] Linchuang Gandanbing Zazhi. 2019;35:737–743.
-
- [Chinese expert consensus on multidisciplinary diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with hepatic vein or inferior vena cave tumor thrombus] Zhongguo Shiyong Waike Zazhi. 2019;6:17–22.
-
- Finn RS, Qin S, Ikeda M, Galle PR, Ducreux M, Kim TY, Kudo M, Breder V, Merle P, Kaseb AO, Li D, Verret W, Xu DZ, Hernandez S, Liu J, Huang C, Mulla S, Wang Y, Lim HY, Zhu AX, Cheng AL IMbrave150 Investigators. Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:1894–1905. - PubMed
-
- Yamamura K, Beppu T, Miyata T, Okabe H, Nitta H, Imai K, Hayashi H, Akahoshi S. Conversion Surgery for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Following Molecular Therapy. Anticancer Res. 2022;42:35–44. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

