Anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy has less efficacy in Richter transformation than in <I>de novo</I> large B-cell lymphoma and transformed low-grade B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 38899351
- PMCID: PMC11532690
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2023.284664
Anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy has less efficacy in Richter transformation than in <I>de novo</I> large B-cell lymphoma and transformed low-grade B-cell lymphoma
Abstract
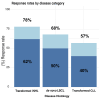
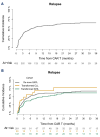
The activity of anti-CD19 chimerci antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) with Richter's transformation (RT) to aggressive large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL) is largely unknown. In a multicenter retrospective study, we report the safety and efficacy of CAR T-cell therapy in patients with RT (N=30) compared to patients with aggressive B-cell lymphoma (N=283) and patients with transformed indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma (iNHL) (N=141) between April 2016 and January 2023. Two-thirds of patients received prior therapy for CLL before RT and 89% of them received B-cell receptor and B-cell lymphoma 2 inhibitors. Toxicities of CAR T-cell therapy in RT were similar to other lymphomas, with no fatalities related to cytokine release syndrome or immune effector-cell associated neurotoxicity synderome. The 100-day overall response rate and complete response rates in patients with RT were 57% and 47%, respectively. With a median follow-up of 19 months, the median overall survival (OS) was 9.9 months in patients with RT compared to 18 months in de novo LBCL and not reached in patients with transformed iNHL. The OS at 12 months was 45% in patients with RT compared with 62% and 75% in patients with de novo LBCL and transformed iNHL, respectively. In a multivariate analysis, worse OS was associated with RT histology, elevated lactate dehydrogenase, and more prior lines of therapy. CAR T-cell therapy can salvage a proportion of patients with CLL and RT exposed to prior targeted agents; however, efficacy in RT is inferior compared to de novo LBCL and transformed iNHL.
Figures

References
-
- Tsimberidou AM, O’Brien S, Khouri I, et al. Clinical outcomes and prognostic factors in patients with Richter’s syndrome treated with chemotherapy or chemoimmunotherapy with or without stem-cell transplantation. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(15):2343-2351. - PubMed
-
- Al-Sawaf O, Robrecht S, Bahlo J, et al. Richter transformation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)-a pooled analysis of German CLL Study Group (GCLLSG) front line treatment trials. Leukemia. 2021;35(1):169-176. - PubMed
-
- Elnair R, Ellithi M, Kallam A, Shostrom V, Bociek RG. Outcomes of Richter’s transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia/ small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL): an analysis of the SEER database. Ann Hematol. 2021;100(10):2513-2519. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

