Combination Targeted Therapy in Relapsed Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
- PMID: 38899693
- PMCID: PMC11192235
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2401532
Combination Targeted Therapy in Relapsed Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
Abstract
Background: The identification of oncogenic mutations in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) has led to the development of drugs that target essential survival pathways, but whether targeting multiple survival pathways may be curative in DLBCL is unknown.
Methods: We performed a single-center, phase 1b-2 study of a regimen of venetoclax, ibrutinib, prednisone, obinutuzumab, and lenalidomide (ViPOR) in relapsed or refractory DLBCL. In phase 1b, which included patients with DLBCL and indolent lymphomas, four dose levels of venetoclax were evaluated to identify the recommended phase 2 dose, with fixed doses of the other four drugs. A phase 2 expansion in patients with germinal-center B-cell (GCB) and non-GCB DLBCL was performed. ViPOR was administered every 21 days for six cycles.
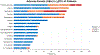
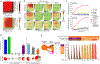
Results: In phase 1b of the study, involving 20 patients (10 with DLBCL), a single dose-limiting toxic effect of grade 3 intracranial hemorrhage occurred, a result that established venetoclax at a dose of 800 mg as the recommended phase 2 dose. Phase 2 included 40 patients with DLBCL. Toxic effects that were observed among all the patients included grade 3 or 4 neutropenia (in 24% of the cycles), thrombocytopenia (in 23%), anemia (in 7%), and febrile neutropenia (in 1%). Objective responses occurred in 54% of 48 evaluable patients with DLBCL, and complete responses occurred in 38%; complete responses were exclusively in patients with non-GCB DLBCL and high-grade B-cell lymphoma with rearrangements of MYC and BCL2 or BCL6 (or both). Circulating tumor DNA was undetectable in 33% of the patients at the end of ViPOR therapy. With a median follow-up of 40 months, 2-year progression-free survival and overall survival were 34% (95% confidence interval [CI], 21 to 47) and 36% (95% CI, 23 to 49), respectively.
Conclusions: Treatment with ViPOR was associated with durable remissions in patients with specific molecular DLBCL subtypes and was associated with mainly reversible adverse events. (Funded by the Intramural Research Program of the National Cancer Institute and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health and others; ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT03223610.).
Copyright © 2024 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
