Hierarchical Protofilament Intertwining Rules the Formation of Mixed-Curvature Amyloid Polymorphs
- PMID: 38899849
- PMCID: PMC11348146
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202402740
Hierarchical Protofilament Intertwining Rules the Formation of Mixed-Curvature Amyloid Polymorphs
Abstract
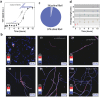
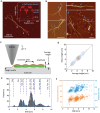
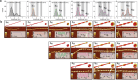
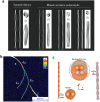
Amyloid polymorphism is a hallmark of almost all amyloid species, yet the mechanisms underlying the formation of amyloid polymorphs and their complex architectures remain elusive. Commonly, two main mesoscopic topologies are found in amyloid polymorphs characterized by non-zero Gaussian and mean curvatures: twisted ribbons and helical fibrils, respectively. Here, a rich heterogeneity of configurations is demonstrated on insulin amyloid fibrils, where protofilament packing can occur, besides the common polymorphs, also in a combined mode forming mixed-curvature polymorphs. Through AFM statistical analysis, an extended array of heterogeneous architectures that are rationalized by mesoscopic theoretical arguments are identified. Notably, an unusual fibrillization pathway is also unraveled toward mixed-curvature polymorphs via the widespread recruitment and intertwining of protofilaments and protofibrils. The results present an original view of amyloid polymorphism and advance the fundamental understanding of the fibrillization mechanism from single protofilaments into mature amyloid fibrils.
Keywords: amyloid polymorphism; atomic force microscopy; filament intertwining mechanism; mixed‐curvature amyloid.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- a) Annamalai K., Gührs K.‐H., Koehler R., Schmidt M., Michel H., Loos C., Gaffney P. M., Sigurdson C. J., Hegenbart U., Schönland S., Fändrich M., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 4822; - PMC - PubMed
- b) Bansal A., Schmidt M., Rennegarbe M., Haupt C., Liberta F., Stecher S., Puscalau‐Girtu I., Biedermann A., Fändrich M., Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1013. - PMC - PubMed
-
- a) Congdon E. E., Wu J. W., Myeku N., Figueroa Y. H., Herman M., Marinec P. S., Gestwicki J. E., Dickey C. A., Yu W. H., Duff K. E., Autophagy 2012, 8, 609; - PMC - PubMed
- b) Fitzpatrick A. W. P., Falcon B., He S., Murzin A. G., Murshudov G., Garringer H. J., Crowther R. A., Ghetti B., Goedert M., Scheres S. H. W., Nature 2017, 547, 185; - PMC - PubMed
- c) Lutter L., Aubrey L. D., Xue W., JMB 2021, 483, 167124. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Laboratory of Biological Electron Microscopy
- RamónyCajalFellowship/MCIN/AEI/ 10.13039/501100011033 and FSE +
- ref.RYC2022-037744-I/MCIN/AEI/ 10.13039/501100011033 and FSE +
- CRSII5_177195/SNSF_/Swiss National Science Foundation/Switzerland
- 310030_188548/SNSF_/Swiss National Science Foundation/Switzerland
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
