Expression of L1 Cell Adhesion Molecule, a Nephronal Principal Cell Marker, in Nephrogenic Adenoma
- PMID: 38901674
- PMCID: PMC11344683
- DOI: 10.1016/j.modpat.2024.100540
Expression of L1 Cell Adhesion Molecule, a Nephronal Principal Cell Marker, in Nephrogenic Adenoma
Abstract
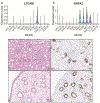
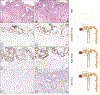
Nephrogenic adenoma (NA) is a benign, reactive lesion seen predominantly in the urinary bladder and often associated with antecedent inflammation, instrumentation, or an operative history. Its histopathologic diversity can create diagnostic dilemmas and pathologists use morphologic evaluation along with available immunohistochemical (IHC) markers to navigate these challenges. IHC assays currently do not designate or specify NA's potential putative cell of origin. Leveraging single-cell RNA-sequencing technology, we nominated a principal (P) cell-collecting duct marker, L1 cell adhesion molecule (L1CAM), as a potential biomarker for NA. IHC characterization revealed L1CAM to be positive in all 35 (100%) patient samples of NA; negative expression was seen in the benign urothelium, benign prostatic glands, urothelial carcinoma (UCA) in situ, prostatic adenocarcinoma, majority of high-grade UCA, and metastatic UCA. In the study, we also used single-cell RNA sequencing to nominate a novel compendium of biomarkers specific for the proximal tubule, loop of Henle, and distal tubule (DT) (including P and intercalated cells), which can be used to perform nephronal mapping using RNA in situ hybridization and IHC technology. Employing this technique on NA we found enrichment of both the P-cell marker L1CAM and, the proximal tubule type-A and -B cell markers, PDZKI1P1 and PIGR, respectively. The cell-type markers for the intercalated cell of DTs (LINC01187 and FOXI1), and the loop of Henle (UMOD and IRX5), were found to be uniformly absent in NA. Overall, our findings show that based on cell type-specific implications of L1CAM expression, the shared expression pattern of L1CAM between DT P cells and NA. L1CAM expression will be of potential value in assisting surgical pathologists toward a diagnosis of NA in challenging patient samples.
Keywords: L1CAM; cell type–specific marker; immunohistochemistry; kidney; nephrogenic adenoma; urothelial carcinoma.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
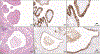



References
-
- Amin W, Parwani AV. Nephrogenic adenoma. Pathol Res Pract. 2010;206(10):659–662. - PubMed
-
- Li L, Williamson SR, Castillo RP, et al. Fibromyxoid Nephrogenic Adenoma: A Series of 43 Cases Reassessing Predisposing Conditions, Clinical Presentation, and Morphology. Am J Surg Pathol. 2023;47(1):37–46. - PubMed
-
- Santi R, Angulo JC, Nesi G, et al. Common and uncommon features of nephrogenic adenoma revisited. Pathol Res Pract. 2019;215(10):152561. - PubMed
-
- Turcan D, Acikalin MF, Yilmaz E, Canaz F, Arik D. Nephrogenic adenoma of the urinary tract: A 6-year single center experience. Pathol Res Pract. 2017;213(7):831–835. - PubMed
-
- Diolombi M, Ross HM, Mercalli F, Sharma R, Epstein JI. Nephrogenic Adenoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2013;37(4):532–538. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

